Stock Buybacks Crash Just As Markets Need Them Most
At the start of January, when the market euphoria was at an all time high, the blow off top meltup was raging and an army of millennial Robinhood daytraders was about to be unleashed (only to be crucified at the end of February), we first warned our readers that “Institutions, Retail And Algos Are Now All-In, Just As Buybacks Tumble.” In the markets, nobody noticed and the warning fell on deaf ears as the relentless melt up, which we called for what it was, namely a clear “distribution” from smart to dumb money – continued.
Exactly two months and one bear market later, the first in 11 years, they finally noticed, with Bloomberg today writing that US companies, which until now were quite happy to sell some BBB-rated bonds and use the proceeds to buy stocks to prop up their stock price, have stepped back from repurchasing their shares even before the coronavirus outbreak (something we made quite clear in January).
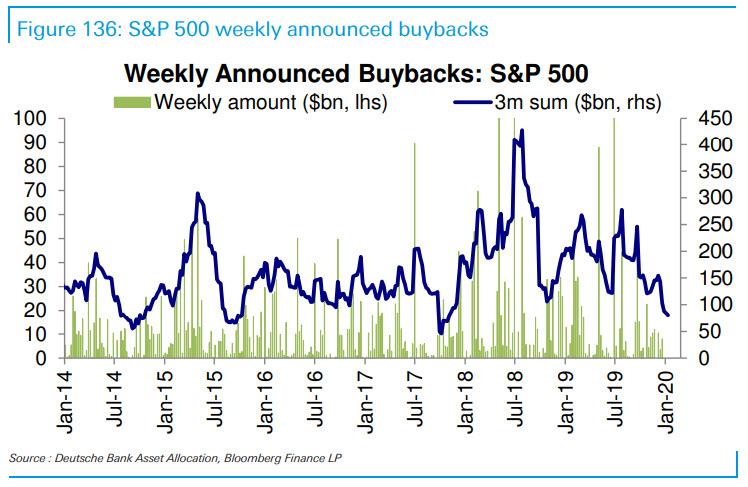
Using a calculation by the permabulls over at Birinyi, Bloomberg reports that companies have announced $122 billion of share repurchases in January and February, which as we warned was the lowest in years and down 46% from a year ago for the biggest drop to start a year since 2009.
The numbers above fail to capture the crash in markets the followed the acute phase of Coronavirus pandemic, as well as the most recent oil plunge that has caused a plunge in oil prices and hammered all junk-bond funded companies. As such, Bloomberg’s reporters correctly point out that the “reduction underlines a concern that will get bigger should the virus inaugurate an age of prudence among corporate treasurers. Luxuries such as share repurchases, while showing signs of picking up amid the rout, are easy to cut when cash preservation and creditworthiness become the priorities.“
Which is not to say that companies do not buyback their stock when markets tumble: indeed during prior corrections, repurchases may have prevented equity losses from snowballing. For example, in the middle of the sell-off in May 2019, repurchases by BofA’s corporate clients surged 23% for the eighth-busiest week in a decade. The market bottomed on the first day of June. During the route in February 2018, the rebound in stocks came in a week when Goldman Sachs’s corporate-trading desk saw the most buyback orders ever.
This time however, with a global recession over the corner, it may be different. Indeed, with companies now rushing to draw down on revolvers in a liquidity procurement panic, the last thing they will be spending money on ahead of the recession is buybacks. In fact, one can argue that the main reason why we are now in a bear market and on the verge of a recession is because of companies such as Boeing, which until recently spent billions on buybacks; companies which are now drawing down on their revolvers.
“If they’re forced to use that for other areas of the business, you’ll lose some of that key support in the market,” said Mike Stritch, chief investment officer for BMO Wealth Management. “That’s a key underpinning for the stock market, and you do worry you’re going to see some companies folding up on this.”
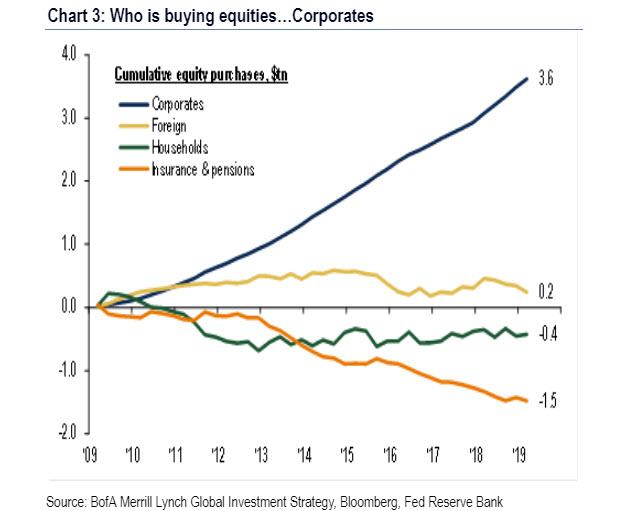
That the disappearance of buybacks is a problem is an understatement: as we reported recently for the past decade, the only source of buying have been companies themselves, repurchasing their stock.
Ironically, while companies should have stopped repurchasing their stock a long time ago, buyback appetite remained strong in recent weeks, and in the final week of February, when the S&P 500 tumbled the most since 2008, Goldman’s corporate clients snapped up their own shares at the fastest rate in two years, with volume running at 2.3 times the average in 2019. Unfortunately, it now appears they used up much of their dry powder just as stocks were about to take another leg lower.
In a perfect world, companies should maximize their buybacks at the lows and halt them at the highs, yet in the real world the opposite happens, even if there are plenty of experts who will tell you what “should” happen, experts such as Don Townswick, director of equity strategies at Conning, who told Bloomberg that “when your stock price is undervalued, buybacks become more attractive. At these levels in the marketplace, smart management is looking at this and thinking, ‘This is the time to actually realize those buybacks. We’re buying our stock 15% below where we thought it was.’”
Ah yes, but what Don is forgetting is that the bulk of buybacks in recent years was debt-funded, and unfortunately right now credit markets are slammed shut which means that companies have to rely on their own cashflow generation and cash balances to fund management’s favorite stock option boosting activity. There is just one problem: as we first reported last year, corporate America’s cash is draining at the fastest rate in decades, with balances at S&P 500 companies excluding financial firms plunging 15% in the past 12 months.
What’s worse is that the market now appears to be frontrunning the inability of companies to prop up their own stock prices, and is punishing those companies that have relied the most on buybacks. As Bloomberg notes, while the whole market is down more than 11% this year through yesterday, the S&P 500 Buyback Index that tracks stocks with the highest payout ratio has fared far worse, falling 19% this year.
Almost as if traders know that the golden goose, that propped up the market on so many occasions in the past, is now dead.
Tyler Durden
Wed, 03/11/2020 – 22:05
via ZeroHedge News https://ift.tt/2W7G82C Tyler Durden