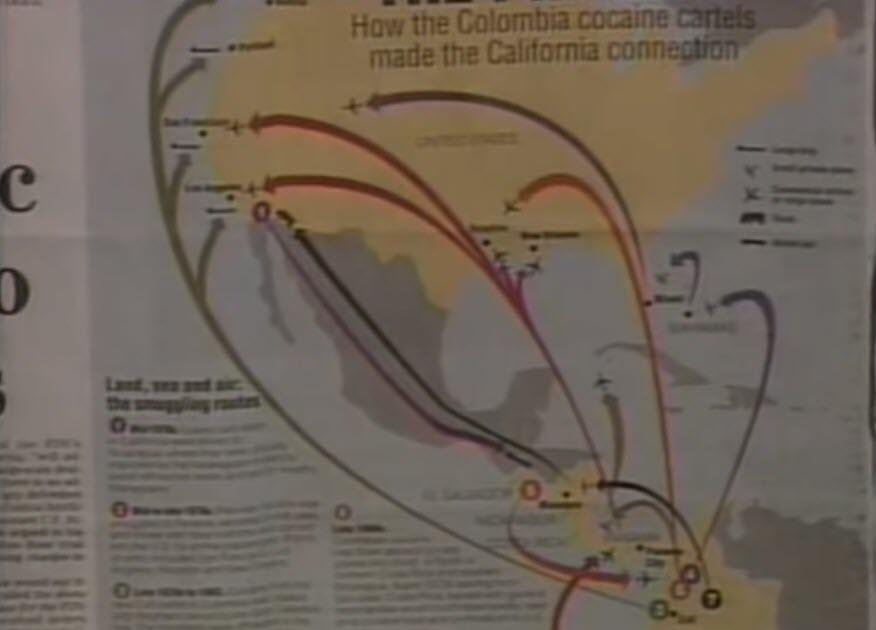
Investigative journalist Robert Parry credits Gary Webb for being responsible for the following government investigations into the Reagan-Bush administration’s conduct of the Contra war:
On December 10, 1996, Los Angeles County Sheriff Sherman Block announced the conclusion of his investigation into the issue, publishing a summary of the investigation at a press conference. He announced at the press conference that “We have found no evidence that the government was involved in drug trafficking in South-Central.” Nevertheless, the report included information that supported some of the charges. Charles Rappleye reported in the L.A. Weekly that Block’s “unequivocal statement is not backed up by the report itself, which raises many questions.” Much of the LAPD investigation centered on allegations made in a postscript article to the newspaper’s “Dark Alliance” series.
On January 29, 1998, Hitz published Volume One of his internal investigation. This was the first of two CIA reports that eventually substantiated many of Webb’s claims about cocaine smugglers, the Nicaraguan contra movement, and their ability to freely operate without the threat of law enforcement.
On March 16, 1998, Hitz admitted that the CIA had maintained relationships with companies and individuals the CIA knew were involved in the drug business. Hitz told the House Permanent Select Committee on Intelligence that “there are instances where CIA did not, in an expeditious or consistent fashion, cut off relationships with individuals supporting the Contra program who were alleged to have engaged in drug-trafficking activity or take action to resolve the allegations.” Senator John Kerry reached similar conclusions a decade earlier in 1987.
On May 7, 1998, Rep. Maxine Waters, revealed a memorandum of understanding – item 24 between the CIA and the Justice Department from 1982, which was entered into the Congressional Record. This letter had freed the CIA from legally reporting drug smuggling by CIA assets, a provision that covered the Nicaraguan Contras and the Afghan rebels.
On July 23, 1998, the Justice Department released a report by its Inspector General, Michael R. Bromwich. The Bromwich report claimed that the Reagan-Bush administration was aware of cocaine traffickers in the Contra movement and did nothing to stop the criminal activity. The report also alleged a pattern of discarded leads and witnesses, sabotaged investigations, instances of the CIA working with drug traffickers, and the discouragement of DEA investigations into Contra-cocaine shipments. The CIA’s refusal to share information about Contra drug trafficking with law-enforcement agencies was also documented. The Bromwich report corroborated Webb’s investigation into Norwin Meneses, a Nicaraguan drug smuggler.
On October 8, 1998, CIA I.G. Hitz published Volume Two of his internal investigation. The report described how the Reagan-Bush administration had protected more than 50 Contras and other drug traffickers, and by so doing thwarted federal investigations into drug crimes. Hitz published evidence that drug trafficking and money laundering had made its way into Reagan’s National Security Council where Oliver North oversaw the operations of the Contras.
According to the report, the Contra war took precedence over law enforcement. To that end, the internal investigation revealed that the CIA routinely withheld evidence of Contra crimes from the Justice Department, Congress and even the analytical division of the CIA itself. Further, the report confirmed Webb’s claims regarding the origins and the relationship of Contra fundraising and drug trafficking. The report also included information about CIA ties to other drug traffickers not discussed in the Webb series, including Moises Nunez and Ivan Gomez. More importantly, the internal CIA report documented a cover-up of evidence which had led to false intelligence assessments.
Webb was widely smeared by the MSM shortly after this interview…
He was eventually vindicated, but not before his career was destroyed.
He was found dead of an apparent suicide in 2004.
The price of being a whistleblower?
Source: The Strategic Culture Foundation
via ZeroHedge News http://bit.ly/2SdiEbS Tyler Durden