Fed Announes First Rate Hike Since 2018 To Stem Soaring Inflation, Bullard Dissents
A little background:
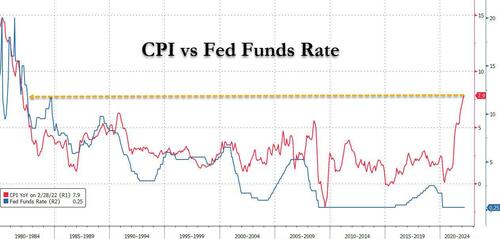
By now, enough has been said about what the Fed may do today: consensus expects that to fight soaring inflation, the Fed will enact a 25bps rate hike (but not 50bps unless Powell really wants to shock markets), the first since 2018, together with forward guidance for a string of hikes. Considering where inflation is, it is very clear by now that the Fed is far behind the curve – the list time CPI was here, the Fed Funds rate was 15%!
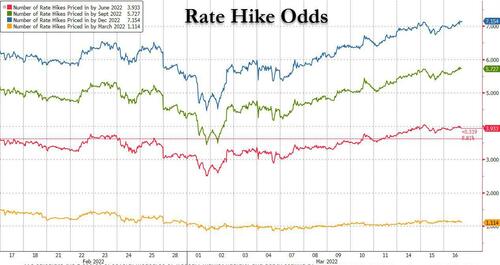
Needless to say, a rate hike has long been priced in by the market which sees more than 100% odds of a 25 bps hike (and small odds of a 50bps rate hike) and more than 7 rate hikes for all of 2022.
Consensus also expects a a mention of Ukraine risk, and while the Fed is not expected to provide details on B/S reduction, it may share a light calendar guide; Consensus also expects dots to be raised to four/five hikes in 2022 at 1.1%/1.4%) but the “terminal rate” dot will unchnaged; elsewhere, the 2022 GDP dot will stay at 3.3% while the Fed raises both the 2022 and 2023 PCE dots.
The FOMC may, of course, surprise either hawkish or dovish. Here is how to determine which way the Fed is leaning:
- Dovish: Any hike dissenters: no forward guidance for hikes in statement; strong concerns over Ukraine in statement FFR 2022 dot £ 0.9%. long run dot < 2.5%: 2022 GDP dot < 3%: mild rises in 2022 PCE dot/no rises in 2023.
- Hawkish: Shock 50bps hike, or any dissenters to just 25bps: no mention of Ukraine risk; concern over long-run inflation expectations; details on B/S reduction; 2022 FFR dot > 1.4; long run FFR dot > 2.5%; 2022 GDP dot > 3 4%: rise in 2024 PCE dot.
Ian Lyngen at BMO Capital Markets is among those in the dovish camp: he anticipates a more cautious liftoff by the Fed than is implied by the futures market: “This isn’t to suggest the chair won’t emphasize the need to address accelerating inflationary pressures with a series of measured and predictable rate increases — after all, this is the beginning of a hiking campaign.”
Before the press briefing, the biggest news should be in the 2022 dot plot, according to Bloomberg. The FOMC was at three hikes in December. That will move up, and economists surveyed by Bloomberg are looking for four hikes, but many Wall Stret economists see five, while markets as noted above, are pricing in around seven hikes, or one at every meeting this year. There’s a plausible case for four, five, six or seven hikes in the new dots. The 2022 dots of course have the likelihood of moving market pricing, which has already moved up over the course of the last few months.
With a hike in the bag, Shawn Cruz, senior market strategist at TD Ameritrade said that “what is going to be interesting is what they say about their intentions for the balance sheet. I think that was a little bit of a surprise for markets when they announced that they were also going to start running off the balance sheet this year, and I wonder if that is maybe at least going to get softened a little bit at the meeting.”
Meanwhile, as Bloomberg’s Ye Xie notes, 2Y yields have moved 160 bps over the past six months, marking the biggest jump at the start of a Fed tightening cycle in modern history. Even so, markets indicate tightening will likely slow from some seven hikes this year to less than two in 2023, before cuts in late 2023/early-to-mid 2024.
Meanwhile, inflation expectations embedded in breakeven rates remain well above the Fed’s target in the next few years (5y BE is at ~3.5%). Taken together, the markets are saying the Fed will front load the tightening, push rates to a neutral, but not too restrictive level, while tolerating inflation above its 2% target for a persistently long period of time. In other words, as Xie concludes, “Jerome Powell is not Paul Volcker.” But we knew that already.
So with that in mind, here is what the Fed just announced:
- Fed Raises Funds Rate Target Range 25 Bps to 0.25%-0.5%
- Fed Says Inflation Elevated, Cites Broader Prices Pressures
- Fed Says Ukraine War May Create Inflation Pressure, Slower Growth
- Fed Forecasts Rates at 2.8% End ‘24, Long-Run Cut to 2.4%
- Fed Median Forecast Sees Inflation at 4.3% End 2022, 2.7% 2023
- Fed Median Shows Unemployment at 3.5% End 2022, 3.5% End 2023
- Fed Raises Ior 25 Bps to 0.4%, Discount Rate Increased to 0.5%
Bullard dissented, opting for a 50bps rate hike!
- James Bullard, who preferred at this meeting to raise the target range for the federal funds rate by 0.5 percentage point to 1/2 to 3/4 percent
Here is a redline of the FOMC statement:
Here is a summary of the Fed’s economic projections:
Longer-run median unemployment rate 4% compares to previous forecast of 4% at Dec. 15, 2021 meeting
- 2022 median jobless rate at 3.5% vs 3.5%
- 2023 median jobless rate at 3.5% vs 3.5%
- 2024 median jobless rate at 3.6% vs 3.5%
Longer-run real GDP median projection of 1.8% compares to previous forecast of 1.8%
- 2022 median GDP growth 2.8% vs 4.0%
- 2023 median GDP growth 2.2% vs 2.2%
- 2024 median GDP growth 2.0% vs 2.0%
Longer run PCE inflation median at 2.0% compares to previous forecast of 2.0%
- 2022 median PCE inflation 4.3% vs 2.6%
- 2023 median PCE inflation 2.7% vs 2.3%
- 2024 median PCE inflation 2.3% vs 2.1%
- 2022 median core PCE inflation 4.1% vs 2.7%
- 2023 median core PCE inflation 2.6% vs 2.3%
- 2024 median core PCE inflation 2.3% vs 2.1%
Longer run Fed funds median at 2.4% compares to previous forecast of 2.5%
- 2022 median Fed funds 1.9% vs 0.9%
- 2023 median Fed funds 2.8% vs 1.6%
- 2024 median Fed funds 2.8% vs 2.1%
It is notable that the Fed’s terminal rate has increased to a whopping 2.75%!
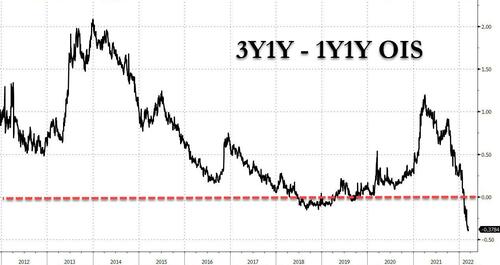
A look at the Fed’s dots suggests that even the Fed is bracing for the coming curve inversion.
Developing
Tyler Durden
Wed, 03/16/2022 – 14:07
via ZeroHedge News https://ift.tt/2ohVywU Tyler Durden