Authored by Jeffrey Tucker via The Brownstone Institute,
The global Covid response was the turning point in public trust, economic vitality, citizen health, free speech, literacy, religious and travel freedom, elite credibility, demographic longevity, and so much more. Now five years following the initial spread of the virus that provoked the largest-scale despotisms of our lives, something else seems to be biting the dust: the postwar neo-liberal consensus itself.

The world as we knew it only a decade ago is on fire, precisely as Henry Kissinger warned in one of his last published articles. Nations are erecting new trade barriers and dealing with citizen uprisings like we’ve never seen before, some peaceful, some violent, and most that could go either way. On the other side of this upheaval lies the answer to the great question: what does political revolution look like in advanced industrial economies with democratic institutions? We are in the process of finding out.
Let’s take a quick march through modern history through the lens of US-China relations.
From the time of China’s opening in the 1980s to the election of Donald Trump in 2016, the volume of trade imports from China only grew, decade after decade. It was the most conspicuous sign of a general trajectory toward globalism that began following the Second World War and accelerated with the end of the Cold War. Tariffs and trade barriers fell ever more, as dollars as the world reserve currency filled the coffers of world central banks. The US was the global source of liquidity that made it all possible.
It came at a huge cost, however, as the US through the decades lost its manufacturing advantages in dozens of industries that once defined the American commercial experience. Watches and clocks, pianos, furniture, textiles, clothing, steel, tools, shipbuilding, toys, household appliances, home electronics, and semiconductors all left US shores while other industries are on the rocks, most especially cars. Today, the much-celebrated “green energy” industries seem fated to be outcompeted as well.
These industries came to be largely replaced by debt-financed financial products, the explosion of the government-backed medical sector, information systems, entertainment, and government-funded education, while the primary exports of the US became debt and petroleum products.
Many forces combined to sweep Donald Trump into office in 2016 but resentment against the internationalization of manufacturing was high among them. As financialization replaced domestic manufacturing, and class mobility stagnated, a political alignment took shape in the US that stunned the elites. Trump got busy on his pet issue, namely erecting trade barriers against countries with whom the US was running trade deficits, primarily China.
By 2018, and in response to new tariffs, the volume of trade with China took its first huge hit, reversing not only a 40-year trajectory of growth but also dealing the first the biggest blow against the 70-year postwar consensus of the neo-liberal world. Trump was doing it largely on his own initiative and against the wishes of many generations of statesmen, diplomats, academics, and corporate elites.
Then something happened to reverse the reversal. That something was the Covid response. In Jared Kushner’s telling (Breaking History), he went to his father-in-law following the lockdowns and said:
We’re scrambling to find supplies all over the world. Right now, we have enough to get through the next week—maybe two—but after that it could get really ugly really fast. The only way to solve the immediate problem is to get the supplies from China. Would you be willing to speak to President Xi to de-escalate the situation?
“Now is not a time to be proud,” said Trump. “I hate that we are in this position, but let’s set it up.”
It’s impossible to imagine the pain that decision must have caused Trump because this move meant a repudiation of all that he believed in foundationally and all that he set out to accomplish as president.
Kushner writes:
I reached out to Chinese ambassador Cui Tiankai and proposed that the two leaders talk. Cui was keen on the idea, and we made it happen. When they spoke, Xi was quick to describe the steps China had taken to mitigate the virus. Then he expressed concern over Trump referring to COVID-19 as the ‘China Virus.’ Trump agreed to refrain from calling it that for the time being if Xi would give the United States priority over others to ship supplies out of China. Xi promised to cooperate. From that point forward, whenever I called Ambassador Cui with a problem, he sorted it out immediately.
What was the result? Trade with China soared. Within a matter of weeks, Americans were wearing Chinese-made synthetic coverings on their faces, having their noses stuck with Chinese-made swabs, and being tended to by nurses and doctors wearing Chinese-made scrubs.
The chart on China’s trade volume looks like this. You can observe the long rise, the dramatic fall from 2018, and the reversal in the volume of PPE purchases following the lockdowns and Kushner’s interventions. The reversal did not last long as trade relations broke down and new trade blocs were born.
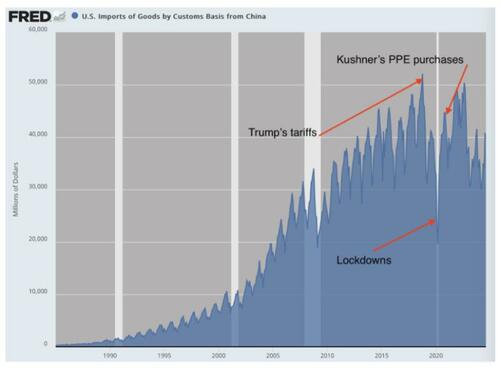
The irony, then, is a salient one: the aborted attempt to restart the neo-liberal order, if that is what it was, occurred in the midst of a global bout of totalitarian controls and restrictions. To what extent were the Covid lockdowns deployed in service of resisting Trump’s decoupling agenda? We have no answers to that question but observing the pattern does leave room for speculation.
Regardless, the trends of 70 years came to be reversed, landing the US in new times, described by the Wall Street Journal in the event of a Trump victory in 2024:
If it turns out that the tariff on China is 60% and the rest of the world is 10%, the U.S.’ average tariff, weighted by the value of imports, would leap to 17% from 2.3% in 2023, and 1.5% in 2016, according to Evercore ISI, an investment bank. That would be the highest since the Great Depression, after Congress passed the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act (1932), which triggered a global surge in trade barriers. U.S. tariffs would go from among the lowest to highest among major economies. If other countries retaliated, the rise in global trade barriers would have no modern precedent.
Talk of the Smoot-Hawley tariff really does plunge us into the wayback machine. Back in those days, trade policy in the US followed the US Constitution (Article I, Section 8). The original system granted Congress the power to regulate commerce with foreign nations, among other powers. This was intended to keep trade policy within the legislative branch to ensure democratic accountability. As a result, Congress responded to the economic/financial crisis by imposing huge barriers against imports. The Depression worsened.
It was a widely accepted belief among many in elite circles that the 1932 tariffs were a factor in the deepening of the economic downturn. Two years later, efforts began to transfer trade authority to the executive so that the legislature would never do something so stupid again. The theory was that the president would be more likely to pursue a free-trade, low-tariff policy. That generation never imagined that the US would elect a president who would use his power to do the opposite.
In the waning days of the Second World War, a group of extremely smart and well-intended diplomats, statesmen, and intellectuals worked to secure the peace in the aftermath of the wreckage in Europe and around the world. They all agreed that a priority in the postwar world was to institutionalize economic cooperation as broadly as possible, under the theory that nations that are dependent on each other for their material well-being were less likely to go to war against each other.
Thus was born what came to be called the neo-liberal order. It consisted of democratic nations with limited welfare states cooperating in trading relationships with ever-lower barriers between states. In particular, the tariff was deprecated as a means of fiscal support and industrial protection. New agreements and institutions were founded to be the administrators of the new system: GATT, IMF, World Bank, and the UN.
The neo-liberal order was never liberal in the traditional sense. It was managed from the outset by states under US dominance. The architecture was always more fragile than it appeared to be. The Bretton Woods agreement of 1944, tightened through the decades, involved nascent institutions of global banking and included a US-managed monetary system that broke down in 1971 and was replaced by a fiat-dollar system. The flaw in both systems had a similar root. They established global money but retained national fiscal and regulatory systems, which thereby disabled the specie-flow mechanisms that smoothed and balanced trade in the 19th century.
One of the consequences was the manufacturing losses mentioned above, which coincided with a growing public perception that the institutions of government and finance were operating without transparency and citizen participation. The ballooning of the security state after 9-11 and the stunning bailouts of Wall Street after 2008 reinforced the point and set the stage for a populist revolt. The lockdowns – disproportionately benefitting elites – plus the burning of cities with the riots of the summer of 2020, the vaccine mandates, and combined with the onset of a migrant crisis, reinforced the point.
In the US, the panic and frenzy all surround Trump but that leaves unexplained why almost every Western country is dealing with the same dynamic. Today the core political fight in the world today concerns nation-states and the populist movements driving them versus the kind of globalism that brought a worldwide response to the virus as well as the worldwide migrant crisis. Both efforts failed spectacularly, most especially the attempt to vaccinate the entire population with a shot that is only defended today by manufacturers and those in their pay.
The problem of migration plus pandemic planning are only two of the latest data points but they both suggest an ominous reality of which many people in the world are newly aware. The nation-states that have dominated the political landscape since the Renaissance, and even back in some cases to the ancient world, had given way to a form of government we can call globalism. It doesn’t refer only to trade across borders. It is about political control, away from citizens in countries toward something else that citizens cannot control or influence.
From the time of the Treaty of Westphalia, signed in 1648, the idea of state sovereignty prevailed in politics. Not every nation needed the same policies. They would respect differences toward the goal of peace. This involved permitting religious diversity among nation-states, a concession that led to an unfolding of freedom in other ways. All governance came to be organized around geographically restricted zones of control.
The juridical boundaries restrained power. The idea of consent gradually came to dominate political affairs from the 18th through the 19th century until after the Great War which dismantled the last of the multinational empires. That left us with one model: the nation-state in which citizens exercised ultimate sovereignty over the regimes under which they live. The system worked but not everyone has been happy with it.
Some of the most high-status intellectuals for centuries have dreamed of global government as a solution to the diversity of policies of nation-states. It’s the go-to idea for scientists and ethicists who are so convinced of the correctness of their ideas that they dream up some worldwide imposition of their favored solution. Humanity has by and large been wise enough not to attempt such a thing beyond military alliances and mechanisms to improve trade flows.
Despite the failure of global management last century, in the 21st century, we’ve seen the intensification of the power of globalist institutions. The World Health Organization (WHO) effectively scripted the pandemic response for the world. Globalist foundations and NGOs seem to be heavily involved in the migrant crisis. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) and World Bank, created as nascent institutions for a global system of money and finance, are exercising outsized influence on monetary and financial policy. The World Trade Organization (WTO) is working to diminish the power of the nation-state over trade policies.
Then there is the United Nations. I happened to be in New York City a few weeks ago when the United Nations met. No question that it was the biggest show on planet Earth. Vast swaths of the city were shut down to cars and buses, with diplomats and heavy-hitting financiers arriving via helicopter on the roofs of luxury hotels, all of which were full for the week of meetings. The prices of everything were jacked up in response since no one was spending his own money in any case.
The attendees were not only statesmen from all over the world but also the biggest financial firms and media outfits, along with representatives of the largest universities and nonprofits. All of these forces seem to be coalescing at once, as if they all want to be part of the future. And that future is one of global governance wherein the nation-state is eventually reduced to pure cosmetics with no operational power.
The impression I had while there was that the experience of everyone in town that day, all swarming around the big United Nations meeting, was one of deep separation of their world from the world of the rest of us. They are “bubble people.” Their friends, source of financing, social groupings, career aspirations, and major influence are detached not only from normal people but from the nation-state itself. The fashionable attitude among them all is to regard the nation-state and its history of meaning as passe, fictional, and rather embarrassing.
Entrenched globalism of the sort that operates in the 21st century represents a shift against and repudiation of half a millennium of the way governance has worked in practice. The United States was initially established as a country of localized democracies that only came together under a loose confederation. The Articles of Confederation created no central government but rather deferred to the former colonies to set up (or continue) their own structures of governance. When the Constitution came along, it created a careful equilibrium of checks and balances to restrain the national state while preserving the rights of the states. The idea here was not to overthrow citizen control over the nation-state but institutionalize it.
All these years later, most people in most nations, the United States especially, believe that they should have final say over the structure of the regime. This is the essence of the democratic ideal, and not as an end in itself but as a guarantor of freedom, which is the principle that drives the rest. Freedom is inseparable from citizen control of government. When that link and that relationship are shattered, freedom itself is gravely damaged.
The world today is packed with wealthy institutions and individuals that stand in revolt against the ideas of freedom and democracy. They do not like the idea of geographically constrained states with zones of juridical power. They believe they have a global mission and want to empower global institutions against the sovereignty of people living in nation-states.
They say that there are existential problems that require the overthrow of the nation-state model of governance. They have a list: infectious disease, pandemic threats, climate change, peacekeeping, cybercrime, financial stability, and the threat of instability, and I’m sure there are others on the list that we’ve yet to see. The idea is that these are necessarily worldwide and evade the capacity of the nation-state to deal with them.
We are all being acculturated to believe that the nation-state is nothing but an anachronism that needs to be supplanted. Keep in mind that this necessarily means treating democracy and freedom as anachronisms too. In practice, the only means by which average people can restrain tyranny and despotism is through voting at the national level. None of us have any influence over the policies of the WHO, World Bank, or IMF, much less over the Gates or Soros Foundations. The way politics is structured in the world today, we are all necessarily disenfranchised in a world governed by global institutions.
And that is precisely the point: to achieve universal disenfranchisement of average people so that the elites can have a free hand in regulating the planet as they see fit. This is why it becomes supremely urgent for every person who aspires to live in peace and freedom to regain national sovereignty and say no to the transfer of authority to institutions over which citizens have no control.
Devolving power from the center is the only path by which we can restore the ideals of the great visionaries of the past like Thomas Jefferson, Thomas Paine, and the entire generation of Enlightenment thinkers. In the end, governing institutions must be in citizen control, and pertain to the borders of particular states, or it necessarily becomes tyrannical over time. As Murray Rothbard put it, we need a world of nations by consent.
There are plenty of reasons to regret the collapse of the neo-liberal consensus and a strong rationale to be concerned about the rise of protectionism and high tariffs. And yet what they called “free trade” (not the simple freedom to buy and sell across borders but rather a state-managed industrial plan) also came at a cost: the transference of sovereignty away from the people in their communities and nations to supranational institutions over which citizens have no control. It did not have to be this way but that is how it was constructed to be.
For that reason, the neo-liberal consensus built in the postwar period contained the seeds of its own destruction. It was too dependent on the creation of institutions beyond people’s control and too reliant on elite mastery of events. It was already crumbling before the pandemic response but it was the Covid controls, nearly simultaneously imposed all over the world to underscore elite hegemony, that exposed the fist under the velvet glove.
The populist revolt of today might someday appear as the inevitable unfolding of events when people become newly aware of their own disenfranchisement. Human beings are not content to live in cages.
Many of us have long predicted a backlash to the lockdowns and all that was associated with them. The full scale of it none of us could have imagined. The drama of our times is as intense as any of history’s great epochs: the fall of Rome, the Great Schism, the Reformation, the Enlightenment, and the fall of the multinational empires. The only question now is whether this ends like America 1776 or France 1790.