Engineering Reality: A Century Of Cultural Control, Part I – The Architecture Of Control
Authored by Joshua Stylman via substack,
A Century of Cultural Control From Edison’s Monopolies to Algorithmic Manipulation
Author’s Note: For years, I understood advertising was designed to manipulate behavior. As someone who studied the mechanics of marketing, I considered myself an educated consumer who could navigate rational market choices. What I didn’t grasp was how this same psychological architecture shaped every aspect of our cultural landscape. This investigation began as curiosity about the music industry’s ties to intelligence agencies. It evolved into a comprehensive examination of how power structures systematically mold public consciousness.
What I discovered showed me that even my most cynical assumptions about manufactured culture barely scratched the surface. This revelation has fundamentally altered not just my worldview, but my relationships with those who either cannot or choose not to examine these mechanisms of control. This piece aims to make visible what many sense but cannot fully articulate – to help others see these hidden systems of influence. Because recognizing manipulation is the first step toward resisting it.
This investigation unfolds in three parts: First, we’ll examine the foundational systems of control established in the early 20th century. Next, we’ll explore how these methods evolved through popular culture and counterculture movements. Finally, we’ll see how these techniques have been automated and perfected through digital systems.
Introduction: The Architecture of Control
In 2012, Facebook conducted a secret experiment on 689,000 users, manipulating their news feeds to study how changes in content affected their emotions. This crude test was just a glimpse of what was coming. By 2024, algorithms would not be used to simply shape what we feel, but what we believe it is even possible to think.
Social media platforms are now able to predict and modify behavior in real-time, while streaming services automatically and continuously curate our cultural consumption, and digital payment systems track every single transaction. What began as simple emotional manipulation has become comprehensive consciousness control.
This power to mold human perception didn’t emerge overnight. The mechanisms of cultural control we see today were built over more than a century, evolving from Edison’s physical monopolies to today’s invisible digital chains. To understand how we arrived at this point of algorithmic consciousness control – and more importantly, how to resist it – we must first trace the historical foundations of these systems and the deliberate architecture of control that shaped them.
The psychological manipulation revealed by the Facebook experiment may seem like a modern phenomenon, but its roots stretch back to the earliest days of mass communication. One of the first architects of cultural control was Thomas Edison, whose establishment of the Motion Picture Patents Company in 1908 laid the groundwork for a century of systematic influence.
Part One: Laying the Foundation
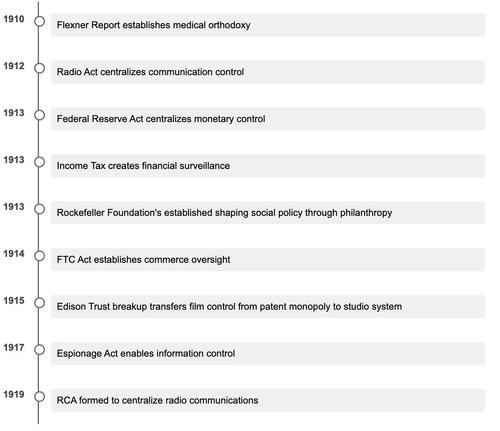
When Thomas Edison established the Motion Picture Patents Company in 1908, he created more than a monopoly – he demonstrated how five key mechanisms could systematically control information and shape consciousness: infrastructure control (film production equipment), distribution control (theaters), legal framework (patents), financial pressure (blacklisting), and legitimacy definition (“authorized” vs “unauthorized” content). These same mechanisms would evolve and reappear across industries and eras, becoming increasingly sophisticated tools for engineering public consciousness and controlling the boundaries of possible thought and expression.
The Rise of Institutional Control
While Edison was establishing control over visual media, a broader system of institutional power was rapidly taking shape. The early 20th century would witness an unprecedented convergence of concentrated control across multiple domains.
When antitrust action broke up the Edison Trust in 1915, control simply shifted from Edison’s patent monopoly to a small group of studios. While presented as creating competition, this “breakup” actually consolidated power in an oligarchy of studios that could more effectively and subversively coordinate content control and messaging – a pattern that would repeat in future antitrust actions.
While the Trust’s breakup appeared to create competition, new forms of control quickly emerged. The Motion Picture Production Code (Hays Code) established in 1934 demonstrated how moral panic could justify systematic content control. Just as Edison had controlled film distribution, the Hays Code controlled what could be depicted on screen, establishing templates for narrative manipulation that would persist into the digital age.
Edison’s template for controlling visual media would soon be replicated across other domains. As I detailed in ‘The Information Factory’, Rockefeller deployed an identical template in medicine: infrastructure control (medical schools), distribution control (hospitals and clinics), legal framework (licensing), financial pressure (strategic funding), and legitimacy definition (“scientific” vs “alternative” medicine). This wasn’t just about eliminating competition – it was about controlling what constituted legitimate knowledge itself.
This wasn’t a coincidence. The early 20th century witnessed unprecedented bureaucratic convergence, as formerly separate domains – medicine, media, education, finance, entertainment, and scientific research – began operating with remarkable coordination. The walls between public institutions, private industry, and government agencies became increasingly permeable. Major foundations played a crucial role in this convergence. The Rockefeller and Ford Foundations, while presenting themselves as philanthropic organizations, effectively shaped academic research priorities and social science methodologies. Through strategic grant-making and institutional support, they helped establish and maintain approved frameworks for understanding society itself. By determining what research got funded and which ideas received institutional backing, these foundations became powerful gatekeepers of acceptable knowledge—extending Rockefeller’s medical model into the broader intellectual sphere.
This unprecedented administrative alignment represented more than coordination – it established interlocking systems for controlling both physical reality and public consciousness. From Edison’s control of visual media to Rockefeller’s definition of medical knowledge to the Federal Reserve’s monetary control, each piece contributed to a comprehensive architecture of social control. What made this system so subtly pervasive was its masterful packaging – each erosion of autonomy was presented as progress, each restriction as protection, each form of control as convenience. The public not only accepted but eagerly embraced these changes, never recognizing that their choices, beliefs, and very understanding of reality were being carefully engineered through institutions they trusted.
The power of this converged system was first demonstrated at scale in profoundly reshaping America’s global role. The narrative of American ‘isolationism’ emerged as one of the most influential shapers of public consciousness. While America had long projected power through banking networks, corporate expansion, and gunboat diplomacy, this reality was gradually reframed and cunningly marketed to an unsuspecting public By establishing a story of American withdrawal from world affairs, advocates for military intervention could position themselves as reluctant modernizers guiding a hesitant nation toward global responsibility. J.P. Morgan’s simultaneous acquisition of major newspapers, controlling 25% of American papers by 1917, helped establish this narrative framework. It wasn’t just about profit – it was about establishing the machinery of public consciousness management in preparation for coming conflicts desired by the ruling class.
By the 1950s, Operation Mockingbird formalized this influence as the CIA systematically infiltrated major media organizations. The program demonstrated how thoroughly intelligence agencies understood the need to shape public perception through seemingly independent channels. Building on methods refined during wartime propaganda efforts, Mockingbird’s techniques would influence everything from news coverage to entertainment programming, establishing templates for information manipulation that continue to evolve today.
What Operation Mockingbird achieved through human editors and planted stories, today’s platforms accomplish automatically through content moderation algorithms and recommendation systems. The same principles of narrative control persist, but the human intermediaries have been replaced by automated systems operating at breathtaking speed on a global scale.
This media-intelligence nexus was exemplified by William S. Paley, who transformed CBS from a small radio network into a broadcasting empire. During World War II, Paley served as supervisor of the Office of War Information (OWI) in the Mediterranean theater before becoming chief of radio in the OWI’s Psychological Warfare Division. His wartime experience in psychological operations directly informed CBS’s postwar programming strategy, where entertainment began to serve as an effective vehicle for social engineering. Under Paley’s leadership, CBS became known as the ‘Tiffany Network,’ masterfully blending entertainment with subtle manipulation techniques refined during his psychological warfare service. This fusion of entertainment and social control would become the template for modern media operations.
This machinery of mass influence would adapt to emerging technologies. By the 1950s, the payola scandal revealed how record companies shaped public consciousness through controlled exposure. Presented as a controversy about DJ bribes, payola actually represented an evolved system for shaping popular taste. The companies controlling these cultural channels maintained deep institutional ties – Paley’s CBS Records continued its military contractor relationships, while RCA’s role in shaping mass culture traced back to its 1919 formation as a Navy-coordinated communications monopoly. Created to maintain domestic control of strategic communications, RCA’s expansion into broadcasting, records and consumer electronics preserved these foundational connections to military and intelligence networks. These methods of cultural control didn’t develop in isolation – they were part of a broader system of social engineering that expanded dramatically during periods of global conflict.
While historians typically treat the World Wars as discrete conflicts, they are better understood as phases in a continuous expansion of social control mechanisms. The infrastructure and methods developed between these conflicts reveals this continuity – the wars provided both the justification and testing grounds for increasingly sophisticated systems of mass psychological manipulation. Military installations like Lookout Mountain Air Force Station in Laurel Canyon weren’t just bases – they were centers for psychological warfare operations, perfectly positioned near the heart of the entertainment industry. Lookout Mountain alone produced over 19,000 classified films, while maintaining high-level connections to Hollywood production
By 1943, this system was so well established that the Office of Strategic Services (OSS) explicitly outlined its strategy in a now-declassified document. Their assessment was unequivocal: motion pictures represented ‘an unparalleled instructional medium’ and ‘a patent force in attitude formation’ that could ‘stimulate or inhibit action.’ The document further stated that the US must ‘exploit the potentialities of the motion picture as a weapon of psychological warfare.’ This wasn’t just about controlling information—it was about fundamentally altering how people understood and experienced reality itself.
While Edison and Rockefeller were establishing physical control systems in America, the entertainment industry was already being integrated into intelligence operations. This pattern stretched back to the industry’s earliest days – Harry Houdini is rumored to have collaborated with British intelligence during World War I, using his performances as cover to gather information in German enclaves. From Charlie Chaplin’s films being analyzed for propaganda potential to Mary Pickford’s war bond drives setting the precedent for celebrity messaging, World War I marked the birth of systematic coordination between Hollywood and intelligence agencies. During World War II, these connections were formalized through the OSS, evolving into today’s Entertainment Liaison Office, through which agencies like the Department of Defense actively shape desired military-themed film narratives.
Sculpting Consciousness of the Masses
While American industries were perfecting control of physical infrastructure and entertainment, British intelligence was developing something even more fundamental – methods to control consciousness itself. Understanding that territorial control was temporary but the power to shape beliefs, desires, and worldviews could be permanent, their innovations would transform social engineering forever. In 1914, they established what began as an innocuous sounding entity called ‘Wellington House,’ which would evolve into increasingly bold bureaucratic iterations – the ‘Department of Information,’ and finally the explicitly Orwellian sounding ‘Ministry of Information.’ Through this organization, they systematized mass psychological manipulation based on new principles – that indirect influence through trusted voices works better than direct propaganda, that emotional resonance matters more than facts, that people trust peer sharing over authority. These psychological principles would become the foundational algorithms of social media platforms a century later. These insights didn’t fade with time – they evolved. When Facebook conducts A/B testing on emotional contagion or social media algorithms promote peer-to-peer sharing over institutional sources, they’re deploying Tavistock’s psychological principles in real-time.
This work evolved through the treatment of shell-shocked soldiers at the Tavistock Clinic (later the Tavistock Institute), where Dr. John Rawlings Rees and his colleagues discovered how psychological trauma could be used to reshape not just individual consciousness, but entire social systems. Through systematic study of trauma and group psychology, they developed methods to shape not just what people could see, but how they would interpret reality itself. The Institute’s work revealed how psychological vulnerability could be used to reshape both individual and group behavior – insights that would prove invaluable as mechanisms of influence evolved from overt censorship to subtle manipulation of perception.
Though largely unknown to the public, Tavistock would become one of the most influential organizations in shaping modern social control methods. While most people today know Tavistock only through recent controversies over gender-affirming care, the institute’s influence extends back generations, shaping cultural narratives and social transformation since its inception. Their current work represents not an anomaly but a continuation of its long-standing mission to reshape human consciousness.
Former MI6 intelligence officer John Coleman’s seminal work The Tavistock Institute of Human Relations provided an insider’s view of its operations. More recently, researchers like Daniel Estulin, Courtenay Turner and Jay Dyer have further examined its profound impact.
The Institute’s most refined achievement was transforming psychological theories into practical tools for cultural engineering, particularly through popular music and youth culture. By embedding their principles into seemingly spontaneous cultural trends, they created a template for social programming invisible to its subjects.
These methods would first be tested through music. The State Department’s jazz diplomacy program of the 1950s-60s revealed how power centers understood music’s potential for cultural design. While Louis Armstrong and Dizzy Gillespie toured as ‘jazz ambassadors,’ another powerful influence was shaping the jazz scene from within. The Baroness Pannonica de Koenigswarter – born into the Rothschild banking dynasty – became a crucial patron of bebop artists like Thelonious Monk and Charlie Parker, both of whom would die in her homes years apart. While her passion for jazz may have been genuine, her deep involvement in the scene coincided with the era when the U.S. State Department and CIA were actively using jazz as a tool of cultural diplomacy. This patronage, whether intentional or not, foreshadowed a pattern of European banking aristocracy’s involvement in supposedly revolutionary musical movements.
In Part Two, we’ll explore the next phase of consciousness control which operated through culture itself. The early experiments in jazz would evolve into an invisible and systematic program of cultural engineering. Institutions would design and ignite cultural movements that appeared organic and by doing so, governing bodies would shape not just what people thought, but their entire framework for understanding anything and everything.
Tyler Durden
Sun, 12/29/2024 – 23:20
via ZeroHedge News https://ift.tt/QyrS9UY Tyler Durden