Goldman Now Sees 2 Rate Cuts In Next 2 Weeks, Expects “Coordinated” Central Bank Easing
It was just Friday that Goldman finally gave up on its bizarrely optimistic global outlook that it had adopted in late 2019, and instead of seeing no rate cuts – or hikes – in 2020, the bank’s chief economist Jan Hatzius capitulated, and said that the Fed will likely cut at least three times in the first half to offset the global economic slowdown due to the coronavirus, late on Sunday, just 48 hours after its first rate forecast revision, Goldman has officially thrown in the towel on even a trace of optimism for the foreseeable future, and now expects not only the Fed to cut 4 times by the end of Q2, but also cautions of a a high risk that the easing it expects over the next several weeks could occur “in coordinated fashion, perhaps as early as the coming week“, which of course is disappointing for all those who were hoping the Fed would step in as soon as Sunday afternoon/evening.
In justifying the implosion of its outlook, Haztius writes that “on Friday morning, we downgraded our baseline view of global GDP growth in 2020 from just over 3% to around 2% on the back of developments related to the coronavirus, with weakness concentrated in the first half of the year. We also changed our Fed call to project 75bp of rate cuts by June, starting with a 25bp cut on March 18.“
This was on Friday morning. Since then, so over the weekend, it appears that newsflow has taken a decided turn for the worse, and as Goldman adds, “the news on the outlook has remained negative, with significant further increases in infections outside of China and an exceptionally weak China PMI release. Moreover, the statement by Fed Chair Powell on Friday afternoon that the Federal Reserve is “closely monitoring” developments and “will use [its] tools and act as needed to support the economy” strongly hints at a rate cut at or even before the March 17-18 FOMC meeting.”
Based on these developments, Goldman is making further adjustment to its Fed call and now projects a 50bp rate cut by March 18 followed by another 50bp of easing in Q2, for a total of 100bp in the first half. Which means that the US Fed Funds rate will be just above zero as the US enters the second half, and has a high chance of tipping negative around the time of the election. Hatzius explains:
The clear signal in Chair Powell’s statement has led the bond market to price in more than 25bp of easing, and the FOMC will not want the cut to come as a disappointment in the present situation.
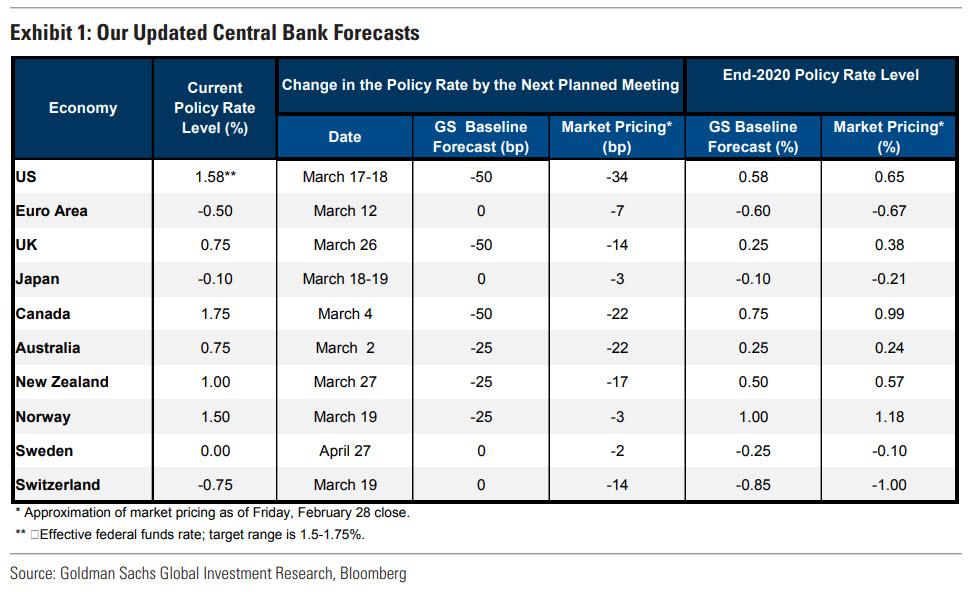
But wait, there’s more: Goldman is now also forecasting rate cuts by most other G10 (and some EM) central banks, including a cumulative 100bp of cuts in Canada, 50bp in the UK, Australia, New Zealand, Norway, India and South Korea, and 10bp in the Euro area and Switzerland. The chart below shows Goldman’s new central bank forecasts along with market pricing as of Friday’s close.
So does 4 rate cuts seem excessive? Not at all, and in fact Goldman even says that relative to some of its new policy rate forecasts, “the risk is on the downside, at least in terms of timing.”
Specifically, we see a high risk that the easing we expect over the next several weeks occurs in coordinated fashion, perhaps as early as the coming week. Chair Powell’s statement on Friday suggests to us that global central bankers are intensely focused on the downside risks from the virus. We suspect that they view the impact of a coordinated move on confidence as greater than the sum of the impacts of each individual move. If a coordinated move does occur, we think some central banks for which we are projecting a first 25bp cut in our new baseline forecast may well join the Fed in cutting by 50bp. This might apply to New Zealand and—if the move occurs very soon—Australia. While it is a close call, our baseline is that the UK and Canada will both cut the policy rate by 50bp at their next meetings, even if a coordinated move does not occur very soon.
Finally to all those who point out the obvious, namely that monetary policy is ill-suited to address the impact of
the virus on the economy, and that it is really public health policy (and fiscal policy more broadly) that needs to act, Goldman agrees “but thinks that central bankers will still want to do their part” to support what Goldman erroneous calls the economy, when it clearly means the market, especially since there is not a trace yet of the US economy being impacted by the coronavirus, and last time we checked, the Fed is not a pre-cog cutting rates in advance of data developments. And while that obvious, what the Fed does do, is cut when stocks tumble, as they have now, and with the world habituated to a central bank bailout any time there is even a modest, 10% correction, this will be the first time we have a global coordinated central bank action in response to… the flu.
Tyler Durden
Sun, 03/01/2020 – 19:20
via ZeroHedge News https://ift.tt/2uOMzws Tyler Durden