Following a full-court press by western nations, the handful of European holdouts – those most reliant on Russian energy supplies and continued Russian capital flows, such as Germany, Hungary, Italy and Cyprus – who have been adverse to expelling Russia from the SWIFT electronic payment-messaging system, are one by one folding on their objections.
Overnight, Italy joined the growing consensus seeking to kick Russia out of the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication global banking system to punish it for the invasion of Ukraine as the European Union weighs up the impact of such an action. Also on Saturday, Poland’s prime minister said he had spoken again with his Hungarian counterpart, Viktor Orban, who had assured him of Budapest’s support for far-reaching sanctions against Russia.
“I talked today again with Prime Minister of Hungary V. (Victor – PAP) Orban. Once again he assured me of support for far-reaching sanctions directed towards Russia. Also including blocking the SWIFT system,” Mateusz Morawiecki wrote on Twitter.
Deputy Foreign Minister Pawel Jabłoński also said on Saturday he had spoken to Hungarian Ambassador Orsolya Zsuzsanna Kovacs and that “Hungary will not block any sanctions against Russia, also including concerning the SWIFT system.”
Meanwhile, Ukrainian Foreign Minister Dmytro Kuleba said on Saturday that Cyprus, which it was thought may have held out against the move, had confirmed it would not block the decision to withdraw Russia from SWIFT.
Finally, Bloomberg reports that Germany has “upended years of policy” and agreed to supply weapons to Kyiv and “look into ways” to shut out Russia from the SWIFT financial messaging system, which however is still a long way away from agreeing to expel Russia.
The German government said in a statement Saturday that it has agreed to the supply of 400 German-made rocket propelled grenades to Ukraine via the Netherlands, along with 14 armored personnel carriers, as well as 1000 anti-tank weapons and 500 Stinger missiles. It will also supply 10,000 tonnes of fuel via Poland. Further supplies to Ukraine are currently being considered, it said.
“After the shameless attack by Russia, Ukraine must be able to defend itself,” German Foreign Minister Annalena Baerbock and Vice Chancellor Robert Habecksaid in the emailed statement. “It has an inalienable right to self-defense.”
At the same time, the government “is working flat out on how to limit the collateral damage of decoupling from SWIFT in such a way that it affects the right people,” they said. “What we need is a targeted and functional restriction of SWIFT.”
The German statement indicates that Europe’s most important nation, and top importer of Russian gas…
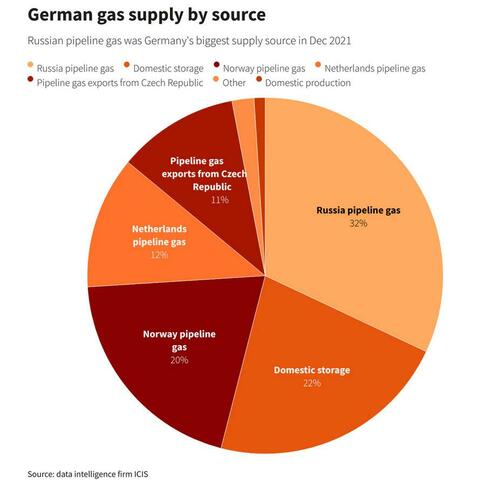
… is still not on the same page as most of its other European peers realizing that an overnight cutoff of Russian gas (something which a SWIFT expulsion would spark) would lead to a crippling hit to the German economy, and instead is seeking a targeted SWIFT cutoff, which course is impossible for the “all or nothing” system. As for the well-known reasons behind Germany’s opposition Erik Meyersson, an economist at Svenska Handelsbanken, put it best: “The EU isn’t on board with removing Russia from SWIFT for one thing because the EU isn’t on board with letting go of Russian energy.”
In effect, the latest German statement is hardly surprising in light of what Germany’s finance minister said on Friday afternoon when he shocked more than a few marketwatchers by saying that ‘we are open to cutting Russia off SWIFT’ with a German government advisor telling RND that “banning Russia from SWIFT is manageable.”
And yet, despite the jawboning Germany is still unwilling (and unable) to pull the plug.
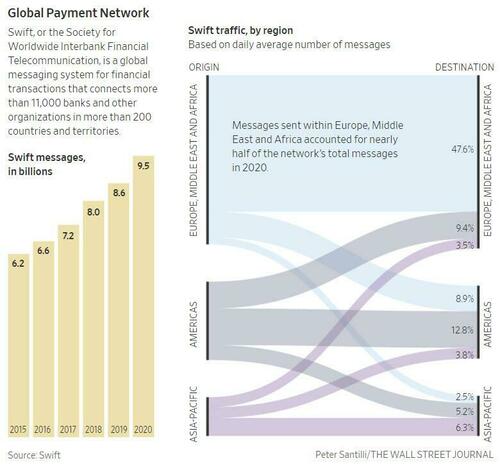
As a reminder, The Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication is the financial-messaging infrastructure that links the world’s banks. The Belgium-based system is run by its member banks and handles millions of daily payment instructions across more than 200 countries and territories and 11,000 financial institutions. Iran and North Korea are already cut off from it, although that has not stopped China from buying millions of barrels of Iranian oil despite US sanctions.
Jumping the shark a but early, Ukraine president Zelensky said he was “grateful to everyone for the decision to cut off Russia from SWIFT”, even though such a decision has not been made (at least not yet).
Others followed suit, such as hedge fund billionaire Bill Ackman, who said in a tweet on Saturday that any SWIFT action would likely result in a quick bank run in Russia:
“I wouldn’t want to keep money in a bank that can’t access the SWIFT system. Once a bank can’t transfer or receive funds from other banks, its solvency can be at risk. If I were Russian, I would take my money out now. Bank runs could begin in Russia on Monday.”
As we reported on Friday, Goldman Sachs’ Allison Nathan asked the question on everyone’s lips: “The removal of Russia from SWIFT – the global electronic payment-messaging system – has been referred to as the “nuclear option” for sanctions. Do you agree with that characterization?”
Eddie Fishman – the former Russia and Europe Lead in the US State Department’s Office of Economic Sanctions Policy and Implementation – responded in a fascinating way:
“No – it’s not even close to being the nuclear option… SWIFT is just a messaging service. If the US and Europe decided to cut Russians banks off from SWIFT without imposing full-blocking sanctions on them, they could still transact with US and European financial institutions – they just couldn’t use SWIFT to do so.”
Fishman went on to point out a potentially even bigger blowback consequence for the West’s actions:
“…and in a perverse way, that may actually increase the demand for SWIFT alternatives, such as Russia’s own System for Transfer of Financial Messages (SPFS).”
And while a decision on SWIFT appears to still be pending, Ackman is certainly correct that is a bank run were to take place it would lead to a deep financial crisis overnight, and may be the reason why – in lieu of a SWIFT expulsion – the U.S. is reportedly weighing sanctions on Russia’s central bank, as Bloomberg reported citing “people familiar with the matter”, a move that would target much of the $643 billion in reserves that Russian President Vladimir Putin had amassed ahead of his invasion of Ukraine.
A final decision hasn’t been made but the Biden administration is urgently considering all options in an attempt to deter Putin from further devastation in Ukraine, the people said, speaking on the condition of anonymity. The U.S. aims to make each move in conjunction with allies across Europe for maximum impact, they said.
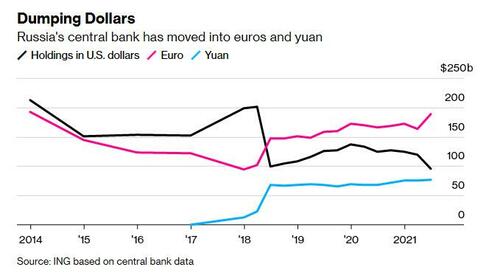
While Russia has been steadily dedollarizing for the past 4 years, and reducing reliance on western foreign currency (while adding to its holdings of yuan and gold), the central bank still held 16.4% of its holdings in dollars at the end of June 2021, according to the latest official data, down from 22.2% a year earlier. The euro’s share was up at 32.2%.
A sanction on the central bank would be “devastating” for Russia, according to Tim Ash, a strategist at Bluebay Asset Management in London. “We would see the ruble crash.”
As Bloomberg notes, although the decision would be without precedent for an economy the size of Russia’s, the U.S. has previously sanctioned the central banks of adversaries. In 2019, the Treasury Department blacklisted the monetary authorities of Iran and Venezuela for funneling money that supported destabilizing activities in the respective regions. North Korea’s central bank is also blacklisted.
Losing access to funds abroad could handcuff Russia’s central bank as it tries to shore up the ruble in the foreign-exchange market by selling hard currency. The direct interventions, announced earlier this week after Putin ordered his military to attack Ukraine, mark the first time the Bank of Russia waded into the market since 2014.
Russia also kept 22% of its hoard in gold, most of which is held domestically and would be out of reach of western sanctions, while about 13% of the central bank’s holdings were in yuan.
Meanwhile, the Biden administration is also debating whether to push for a directive from the European Union needed to ban Russia from SWIFT, though a U.S. and EU decision isn’t imminent especially with Germany still unable to fully make up its mind.
“It appears the Biden administration is gradually coming around to adopting the real hard-hitting sanctions that it should have imposed days ago,” said Marshall Billingslea, who served in the Treasury’s sanctions unit during the Trump administration.