The bursting of the higher education bubble has finally struck its first blow, and it is a serious one. Several major public universities have announced multimillion dollar budget cuts in January, citing enrollment declines among other factors. Pennsylvania State University expects to cut $94 million from its budget starting in July 2025. The University of Connecticut (UConn) announced significant budget cuts in response to its projected $70 million deficit. And the University of New Hampshire (UNH) will slash expenses by $14 million.
These cuts were a long time coming—higher education is facing an enrollment cliff, even as it continues to spend on administration and student services like there’s no tomorrow. Pandemic-era emergency funding could only hold off the reckoning for so long. As university administrators rush to blame their state governments for providing insufficient funds, state legislators should remain staunch in enforcing fiscal discipline on universities. There’s still a long way to go to make higher education cost-effective.
Though university administrators and faculty consider these budget cuts to be nothing short of catastrophic for university operations, some of the cuts appear quite reasonable. For instance, Penn State plans to scale back branch campus operations and cut duplicate programs. This is a necessary step in the right direction—Pennsylvania is known as the “state with too many campuses,” and steep enrollment declines at branch campuses justify reducing their operations.
But even when making the right decisions, universities are too trepidatious. UNH, for example, will cut certain programs at its Aulbani J. Beauregard Center for Equity, Justice, and Freedom. Yet they have not indicated whether only staff or the entire department would be cut. This is not nearly far enough: Not only are diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) administrative units like the Beauregard Center unnecessary and expensive, but they are also harmful to the campus environment. DEI initiatives have led universities to monitor what students and faculty say through bias reporting systems and filtered faculty hiring based on race and political views. Budget cuts should not be needed to cut down on these departments—they should never have been created in the first place.
Instead of making further cuts to superfluous administrators, UNH was quick to close its 60-year-old art museum. The museum housed art that faculty regularly incorporated into classes. Some estimate that the art museum operated at just under $1 million annually. The university could have pursued cuts to other departments before going after a key academic institution. Notably, UNH spends more than $1 million on base salaries for DEI staff alone. This estimate is conservative: It excludes benefits, departmental costs, and other roles at the university related to DEI.
UConn’s drastic approach also demonstrates the misguided priorities of higher education leadership. They announced 15 percent cuts across the board, to be doled out equally over the next five years among all units including administration. This approach might seem more “fair,” but it operates on the faulty assumption that waste is concentrated equally among all parts of the university. We know this is not true: report after report has discussed the issues of administrative bloat and extravagant student services. There’s no need to target core educational functions when more low-hanging fruit exists.
These budget cuts have revived the longstanding fights over public subsidies to higher education institutions. Leaders at Penn State and UConn have publicly called out their state legislatures for failing to fund them to their desired amounts. UConn has discussed raising tuition, and Penn State refuses to commit to a tuition freeze even if their funding demands are met. The arguments hark back to debates over state disinvestment in higher education, in which universities claimed that the exorbitant tuition increases over the past several decades had less to do with massive growth in student loan availability and more to do with reductions in state funding.
But the facts simply do not line up with administrators’ narrative. In the case of UConn, the reduction in state funding is not so much a funding cut as it is a return to pre-pandemic realities. Starting in 2020, the Connecticut state government used pandemic relief funds to provide emergency support to its public universities. The relief funds are set to run out in 2025, and the state has not agreed to cover the gap. This makes the current situation an inevitability: pandemic-era relief funds were temporary, but UConn has apparently budgeted as if they were permanent.
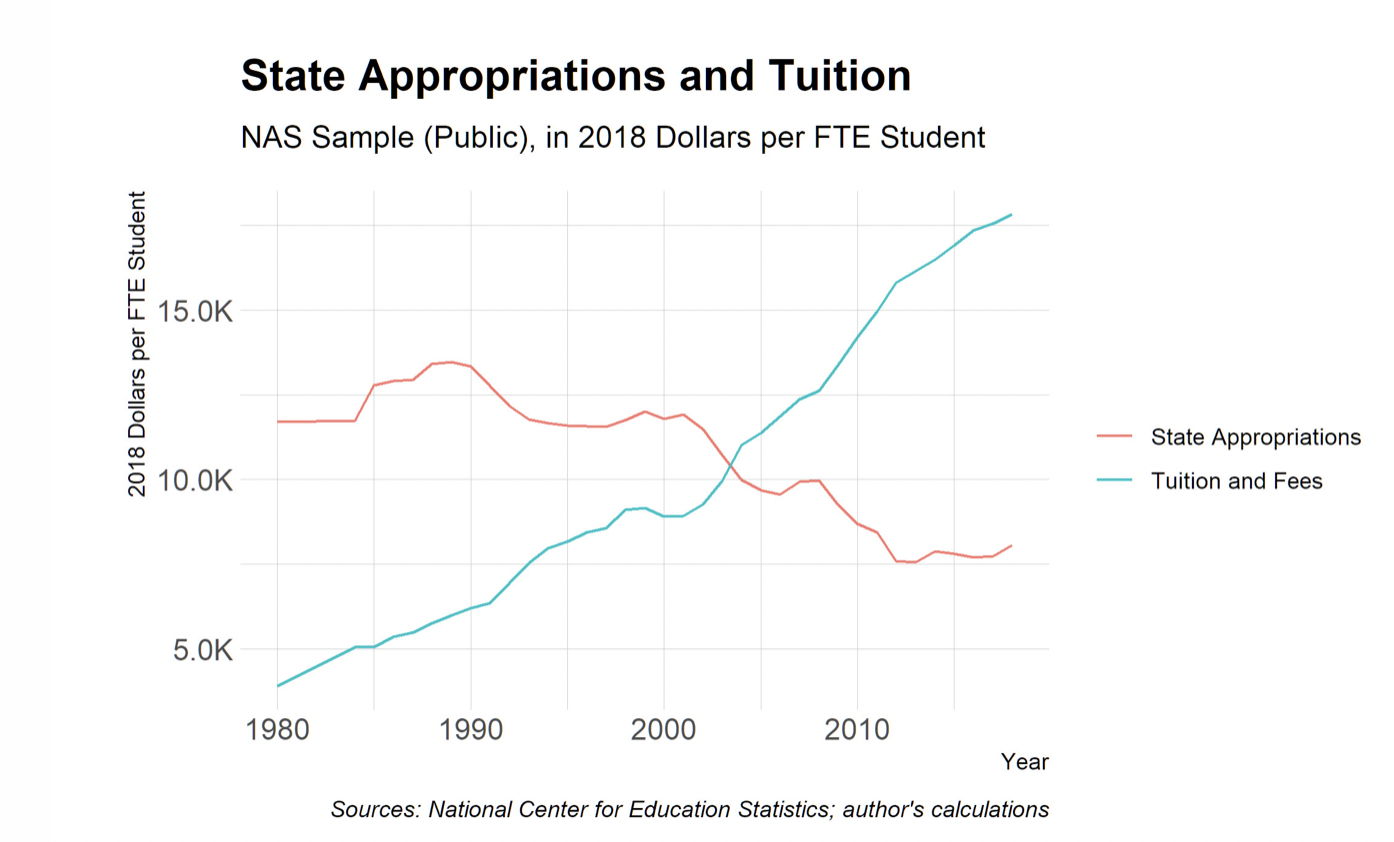
As for increasing tuition, a National Association of Scholars report found that even as state funding per student decreased by nearly $4,000, public universities increased tuition by almost $14,000 per student. State funding decreases alone do not come close to explaining tuition increases. What does explain the increase in tuition is the rapid increase in university expenditures. This is why implementing budget cuts is crucial.
As higher education mourns, taxpayers should welcome budget cuts. Restoring fiscal discipline, though painful in the moment, is the only way to permanently fix our higher education system.
The post University Budget Cuts Were Overdue appeared first on Reason.com.
from Latest https://ift.tt/rvb812o
via IFTTT