Authored by Nick Corbishley via NakedCapitalism.com,
So why are journalists not covering it?
Michael Capuzzo, a New York Times best-selling author , has just published an article titled “The Drug That Cracked Covid”. The 15-page article chronicles the gargantuan struggle being waged by frontline doctors on all continents to get ivermectin approved as a Covid-19 treatment, as well as the tireless efforts by reporters, media outlets and social media companies to thwart them.
Because of ivermectin, Capuzzo says, there are “hundreds of thousands, actually millions, of people around the world, from Uttar Pradesh in India to Peru to Brazil, who are living and not dying.” Yet media outlets have done all they can to “debunk” the notion that ivermectin may serve as an effective, easily accessible and affordable treatment for Covid-19. They have parroted the arguments laid out by health regulators around the world that there just isn’t enough evidence to justify its use.
For his part, Capuzzo, as a reporter, “saw with [his] own eyes the other side [of the story]” that has gone unreported, of the many patients in the US whose lives have been saved by ivermectin and of five of the doctors that have led the battle to save lives around the world, Paul Marik, Umberto Meduri, José Iglesias, Pierre Kory and Joe Varon. These are all highly decorated doctors. Through their leadership of the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care (FLCCC) Alliance, they have already enhanced our treatment of Covid-19 by discovering and promoting the use of Corticoid steroids against the virus. But their calls for ivermectin to also be used have met with a wall of resistance from healthcare regulators and a wall of silence from media outlets.
“I really wish the world could see both sides,” Capuzzo laments.
But unfortunately most reporters are not interested in telling the other side of the story. Even if they were, their publishers would probably refuse to publish it.
That may explain why Capuzzo, a six-time Pulitzer-nominated journalist best known for his New York Times-bestselling nonfiction books Close to Shore and Murder Room, ended up publishing his article on ivermectin in Mountain Home, a monthly local magazine for the of the Pennsylvania mountains and New York Finger Lakes region, of which Capuzzo’s wife is the editor.

It’s also the reason why I decided to dedicate today’s post to Capuzzo’s article. Put simply, as many people as possible –particularly journalists — need to read his story.
As Capuzzo himself says, “I don’t know of a bigger story in the world.”
Total News Blackout
On December 8 2020, FLCCC member Dr Pierre Kory gave nine minutes of impassioned testimony to the US Homeland Security Committee Meeting on the potent anti-viral, anti-inflammatory benefits of ivermectin.

A total of 9 million people (myself included) saw the video on YouTube before it was taken down by YouTube’s owner, Google. As Capuzzo exhaustively lays out, both traditional and social media have gone to extraordinary lengths to keep people in the dark about ivermectin. So effective has this been that even in some of the countries that have benefited most from its use (such as Mexico and Argentina) many people are completely unaware of its existence. And this is no surprise given how little information is actually seeping out into the public arena.
A news blackout by the world’s leading media came down on Ivermectin like an iron curtain. Reporters who trumpeted the COVID-19 terror in India and Brazil didn’t report that Ivermectin was crushing the P-1 variant in the Brazilian rain forest and killing COVID-19 and all variants in India. That Ivermectin was saving tens of thousands of lives in South America wasn’t news, but mocking the continent’s peasants for taking horse paste was. Journalists denied the world knowledge of the most effective life-saving therapies in the pandemic, Kory said, especially among the elderly, people of color, and the poor, while wringing their hands at the tragedy of their disparate rates of death.
Three days after Kory’s testimony, an Associated Press “fact-check reporter” interviewed Kory “for twenty minutes in which I recounted all of the existing trials evidence (over fifteen randomized and multiple observational trials) all showing dramatic benefits of Ivermectin,” he said. Then she wrote: “AP’S ASSESSMENT: False. There’s no evidence Ivermectin has been proven a safe or effective treatment against COVID-19.” Like many critics, she didn’t explore the Ivermectin data or evidence in any detail, but merely dismissed its “insufficient evidence,” quoting instead the lack of a recommendation by the NIH or WHO. To describe the real evidence in any detail would put the AP and public health agencies in the difficult position of explaining how the lives of thousands of poor people in developing countries don’t count in these matters.
Not just in media but in social media, Ivermectin has inspired a strange new form of Western and pharmaceutical imperialism. On January 12, 2021, the Brazilian Ministry of Health tweeted to its 1.2 million followers not to wait with COVID-19 until it’s too late but “go to a Health Unit and request early treatment,” only to have Twitter take down the official public health pronouncement of the sovereign fifth largest nation in the world for “spreading misleading and potentially harmful information.” (Early treatment is code for Ivermectin.) On January 31, the Slovak Ministry of Health announced its decision on Facebook to allow use of Ivermectin, causing Facebook to take down that post and removed the entire page it was on, the Ivermectin for MDs Team, with 10,200 members from more than 100 countries.
In Argentina, Professor and doctor Hector Carvallo, whose prophylactic studies are renowned by other researchers, says all his scientific documentation for Ivermectin is quickly scrubbed from the Internet. “I am afraid,” he wrote to Marik and his colleagues, “we have affected the most sensitive organ on humans: the wallet…” As Kory’s testimony was climbing toward nine million views, YouTube, owned by Google, erased his official Senate testimony, saying it endangered the community. Kory’s biggest voice was silenced.
“The Most Powerful Entity on Earth”
Malcom X once called the media “the most powerful entity on the earth.” They have, he said, “the power to make the innocent guilty and to make the guilty innocent, and that’s power. Because they control the minds of masses”. Today, that power is now infused with the power of the world’s biggest tech and social media companies. Together social and traditional media have the power to make a medicine that has saved possibly millions of lives during the current pandemic disappear from the conversation. When it is covered, it’s almost always in a negative light. Some media organizations, including the NY Times, have even prefaced mention of the word “ivermectin” — a medicine that has done so much good over its 40-year lifespan that its creators were awarded the Nobel Prize for Medicine in 2015 — with the word “controversial.”
Undeterred, many front-line doctors have tried to persuade their respective health regulators of the unparalleled efficacy and safety of ivermectin as a covid treatment. They include Dr. Tess Lawrie, a prominent independent medical researcher who, as Capuzzo reports, evaluates the safety and efficacy of drugs for the WHO and the National Health Service to set international clinical practice guidelines:
“[She] read all twenty-seven of the Ivermectin studies Kory cited. The resulting evidence is consistent and unequivocal,” she announced, and sent a rapid meta-analysis, an epidemiolocal statistical multi-study review considered the highest form of medical evidence, to the director of the NHS, members of parliament, and a video to Prime Minister Boris Johnson with “the good news… that we now have solid evidence of an effective treatment for COVID-19…” and Ivermectin should immediately “be adopted globally and systematically for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19.”
Ignored by British leaders and media, Lawrie convened the day-long streaming BIRD conference—British Ivermectin Recommendation Development—with more than sixty researchers and doctors from the U.S., Canada, Mexico, England, Ireland, Belgium, Argentina, South Africa, Botswana, Nigeria, Australia, and Japan. They evaluated the drug using the full “evidence-to-decision framework” that is “the gold standard tool for developing clinical practice guidelines” used by the WHO, and reached the conclusion that Ivermectin should blanket the world.
“Most of all you can trust me because I am also a medical doctor, first and foremost,” Lawrie told the prime minster, “with a moral duty to help people, to do no harm, and to save lives. Please may we start saving lives now.” She heard nothing back.
Ivermectin’s benefits were also corroborated by Dr. Andrew Hill, a renowned University of Liverpool pharmacologist and independent medical researcher, and the senior World Health Organization/UNITAID investigator of potential treatments for COVID-19. Hill’s team of twenty-three researchers in twenty-three countries had reported that, after nine months of looking for a COVID-19 treatment and finding nothing but failures like Remdesivir— “we kissed a lot of frogs”— Ivermectin was the only thing that worked against COVID-19, and its safety and efficacy were astonishing—“blindingly positive,” Hill said, and “transformative.” Ivermectin, the WHO researcher concluded, reduced COVID-19 mortality by 81 percent.
Why All the Foot Dragging?
Yet most health regulators and governments continue to drag their feet. More evidence is needed, they say. All the while, doctors in most countries around the world have no early outpatient medicines to draw upon in their struggle against the worst pandemic in century. Drawing on his own experience, Capuzzo describes the absence of treatments for COVID-19 as a global crisis:
When my daughter Grace, a vice president at a New York advertising agency, came down with COVID-19 recently, she was quarantined in a “COVID hotel” in Times Square with homeless people and quarantining travelers. The locks on her room door were removed. Nurses prowled the halls to keep her in her room and wake her up every night to check her vitals—not to treat her, because there is no approved treatment for COVID-19; only, if her oxygen plummeted, to move her to the hospital, where there is only a single eective approved treatment for COVID-19, steroids that may keep the lungs from failing.
There are three possible explanations for health regulators’ refusal to allow the use of a highly promising, well-tolerated off-label medicine such as ivermectin:
-
As a generic, ivermectin is cheap and widely available, which means there would be a lot less money to be made by Big Pharma if it became the go-to early-stage treatment against covid.
-
Other pharmaceutical companies are developing their own novel treatments for Covid-19 which would have to compete directly with ivermectin. They include ivermectin’s original manufacturer, Merck, which has an antiviral compound, molnupiravir, in Phase 3 clinical trials for COVID-19. That might explain the company’s recent statement claiming that there is “no scientific basis whatsoever for a potential therapeutic effect of ivermectin against COVID-19.
-
If approved as a covid-19 treatment, ivermectin could even threaten the emergency use authorisation granted to covid-19 vaccines. One of the basic conditions for the emergency use authorisation granted to the vaccines currently being used against covid is that there are no alternative treatments available for the disease. As such, if ivermectin or some other promising medicine such as fluvoxamine were approved as an effective early treatment for Covid-19, the vaccines could be stripped of authorisation.
This may explain why affordable, readily available and minimally toxic drugs are not repurposed for use against Covid despite the growing mountains of evidence supporting their efficacy.
Ivermectin has already been approved as a covid-19 treatment in more than 20 countries. They include Mexico where the mayor of Mexico City, Claudia Scheinbaum, recently said that the medicine had reduced hospitalisations by as much as 76%. As of last week, 135,000 of the city’s residents had been treated with the medicine. The government of India — the world’s second most populous country and one of the world’s biggest manufacturers of medicines — has also recommended the use of ivermectin as an early outpatient treatment against covid-19, in direct contravention of WHO’s own advice.
Dr Vikas P. Sukhatme, the dean of Emory School of Medicine, recently wrote in a column for the Times of India that deploying drugs such as ivermectin and fluvoxamine in India is likely to “rapidly reduce the number of COVID-19 patients, reduce the number requiring hospitalization, supplemental oxygen and intensive care and improve outcomes in hospitalized patients.”
Four weeks after the government included ivermectin and budesonide among its early treatment guidelines, the country has recorded its lowest case count in 40 days.
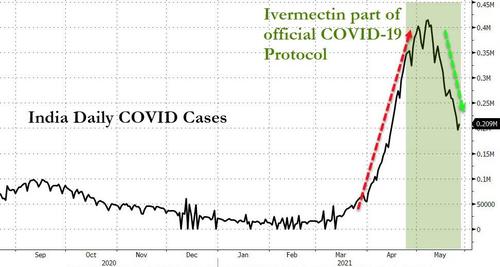
In many of India’s regions the case numbers are plunging in almost vertical fashion. In the capital Delhi, as in Mexico City, hospitalisations have plummeted. In the space of 10 days ICU occupancy fell from 99% to 70%. Deaths are also falling. The test positivity ratio slumped from 35% to 5% in just one month.
One of the outliers of this trend is the state of Tamil Nadu, where cases are still rising steeply. This may have something to do with the fact that the state’s newly elected governor, MK Stalin, decided to exclude ivermectin from the region’s treatment protocol in favor of Remdesivir. The result? Soaring cases. Late last week, Stalin reversed course once again and readopted ivermectin.
For the moment deaths in India remain extremely high. And there are concerns that the numbers are being under-reported. Yet they may also begin to fall in the coming days. In all of the countries that have used ivermectin widely, fatalities are the last thing to fall, after case numbers and hospitalizations. Of course, there’s no way of definitively proving that these rapid falloffs are due to the use of ivermectin. Correlation, even as consistent as this, is not causation. Other factors such as strict lockdowns and travel restrictions no doubt also play a part.
But a clear pattern across nations and territories has formed that strongly supports ivermectin’s purported efficacy. And that efficacy has been amply demonstrated in three meta-analyses.
India’s decision to adopt ivermectin, including as a prophylaxis in some states, is already a potential game-changer. As I wrote three weeks ago, if case numbers, hospitalizations and fatalities fall in India as precipitously as they have in other countries that have adopted ivermectin, it could even become a watershed moment. But for that to happen, the news must reach enough eyes and ears. And for that to happen, reporters must, as Capuzzo says, begin to do their job and report both sides of this vital story.