A $50 Billion Hole Emerges In Trump’s China Trade Deal
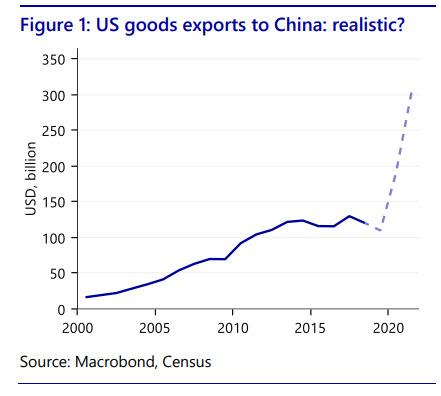
Now that the dust has settled on the US-China trade deal and analysts have had some time to pore over its 90+ pages, various chapters and (non-binding) terms that comprise the body of the agreement, one high-level observation noted by Rabobank, is that the agreement foresees the total amount of goods exports from the US to China to reach above $ 290BN by end-2021. The implication of this is that the chart for US exports to China should basically look like this for the next two years:
As Rabobank’s senior economist Bjorn Giesbergen writes, there are probably very few economists that would deem such a trajectory feasible (except for the perpetually cheerful economics team at Goldman, of course), seeing that it took the US more than 15 years to raise exports from around USD16bn in 2000 to USD 130bn in 2017. Moreover, the Chinese purchases of goods are beneficial to US companies, but at the cost of other countries, and the agreement is only for two years. If China will buy more aircraft from the US, that could be to the detriment of the EU.
According to the document “the parties project that the trajectory of increases … will continue in calendar years 2020 through 2025.” But “to project” does not sound as firm as “shall ensure.” So, as the Rabo economist asks, “are we going to see a repetition of the 2019 turmoil caused by the phase 1 trade negotiations after those two years? Or is this supposed to be solved in the phase 2 deal that is very unlikely to be made? What’s more, while the remaining tariffs provide leverage for US trade negotiators, they are still a tax on US importers and US consumers of Chinese goods.”
But before we even get there, going back to the chart shown above, Bloomberg today points out something we have pointed out in the past, namely that China’s $200 billion, two-year spending spree negotiated with the Trump administration appears increasingly difficult to deliver, and now a $50 billion “hole” appears to have opened up: that is the amount of U.S. exports annually left out and many American businesses still uncertain about just what the expectations are.
Some background: while Trump officials stressed the reforms aimed at curbing intellectual-property theft and currency manipulation that China has agreed to in the “phase one” trade deal signed Wednesday, the Chinese pledge to buy more American exports has become an emblem of the deal to critics and supporters alike.
The administration has said those new exports in manufactured goods, energy, farm shipments and services will come over two years on top of the $130 billion in goods and $57.6 billion in services that the U.S. sent to China in 2017 — the year before the trade war started and exports were hit by Beijing’s retaliatory measures to President Donald Trump’s tariffs.
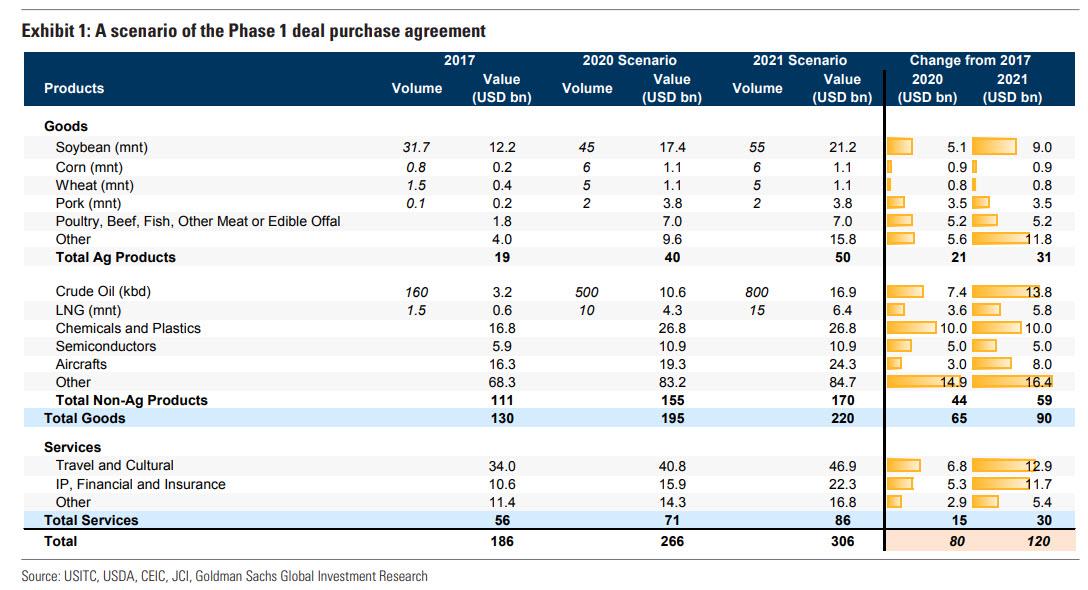
And while Goldman said it is certainly feasible that China can ramp up its purchases of US goods, going so far as providing a matrix “scenario” of what such purchases could look like…
… that now appears virtually impossible, because as Bloomberg notes, the list of goods categories in the agreement covers a narrower group of exports to China that added up to $78.8 billion in 2017, or $51.6 billion less than the overall goods exports to the Asian nation that year. The goods trade commitment makes up $162.1 billion of the $200 billion total, with $37.9 billion to come from a boost in services trade such as travel and insurance.
Here, the math gets even more ridiculous:
The target for the first year that the deal takes effect is to add $63.9 billion in manufactured goods, agriculture and energy exports. According to Bloomberg economist Maeva Cousin’s analysis, that would be an increase of 81% over the 2017 baseline. In year two, the agreement calls for $98.2 billion surge in Chinese imports, which would require a 125% increase over 2017.
Importantly for China, the deal requires those purchases to be “made at market prices based on commercial considerations,” a caveat which spooked commodities traders, and led to a sharp drop in ags in the day following the deal’s announcement.
Can China pull this off? Yes, if Beijing tears up existing trade deals and supply chains and imposes explicit procurement targets and demands on China’s local business. As Bloomberg notes, “critics argue that such pre-ordained demand amounts to a slide into the sort of government-managed trade that U.S. presidents abandoned decades ago” and the very sort of act of central planning that U.S. officials have, paradoxically, spent years trying to convince China to walk away from.
This may also explain why a key part of the trade deal will remain secret: the purchase plan is based on what the administration insists is a specific – if classified – annex of Chinese commitments. “The 20-page public version of that annex lists hundreds of products and services from nuclear reactors to aircraft, printed circuits, pig iron, soybeans, crude oil and computer services but no figures for purchases.“
Going back to the critics, it is this convoluted mechanism that has them arguing that China’s stated targets will likely never be met: “This is ambitious and it will create some stresses within the supply system,” said Craig Allen, the president of the U.S.-China Business Council.
That’s not all: as Allen said, among the outstanding questions was whether China would lift its retaliatory duties on American products as the US keeps its tariffs on some $360 billion in imports from China as Trump seeks to maintain leverage for a second phase of negotiations. Allen also made clear the overall purchase schedule left many U.S. companies uncomfortable even as they saw benefits in other parts of the deal. “The vast majority of our members are looking for no more than a level playing field in China,” Allen said. “We are not looking for quotas or special treatment.”
As a result, for many manufacturers what is actually changing – and what China has committed to instead of given a “best efforts” promise to achieve – remains unclear.
Major exporters such as Boeing Co., whose CEO Dave Calhoun attended Wednesday’s signing ceremony, have stayed mum about what exactly the deal will mean for their business with China. In an attempt to “clarify”, Trump tweeted that the deal includes a Chinese commitment to buy $16 billion to $20 billion in Boeing planes. It was unclear if he meant 737 MAX planes which nobody in the world will ever voluntarily fly inside again.
Finally, prompting the latest round of cronyism allegations, Trump’s new China pact also includes plans for exports of American iron and steel, “a potential gain for an industry close to the president that has benefited from his tariffs and complained about Chinese production and overcapacity for years.” As Bloomberg adds, the text of the agreement lists iron and steel products ranging from pig iron to stainless steel wire and railway tracks, but steel industry sources said they had been caught by surprise and not been given any additional details on China’s purchase commitments.
It is unclear why Beijing would need US products: after all, in its scramble to erect ghost cities and hit a goalseeked GDP print, China produces more than 50% of the world’s steel, drawning criticism from around the world – if not Greta Thunberg – for the massive coal-derived pollution that comes from flooding global markets with cheap steel.
Tyler Durden
Fri, 01/17/2020 – 15:30
via ZeroHedge News https://ift.tt/375baLk Tyler Durden