Nomura: “The Market Has Only Just Begun Staring Into The Abyss”
While many post-mortems will be written on what, despite Friday’s torrid 9% rebound, has been a historic, unforgettable week which saw the US stock market plunge the most since the worst days of the global financial crisis, one of the more detailed and impactful was that of Nomura’s quant Masanari Takada who put the week’s events in simple, easy to understand context: “In little more than the blink of an eye, the situation has come to look like the 2008 Lehman Brothers crisis all over again.”
Below we repost some of the key points from his note as we brace for another historic week, especially since something tells us – perhaps the Fed’s failure to normalize the funding situation – that the events from next week will be even more memorable.
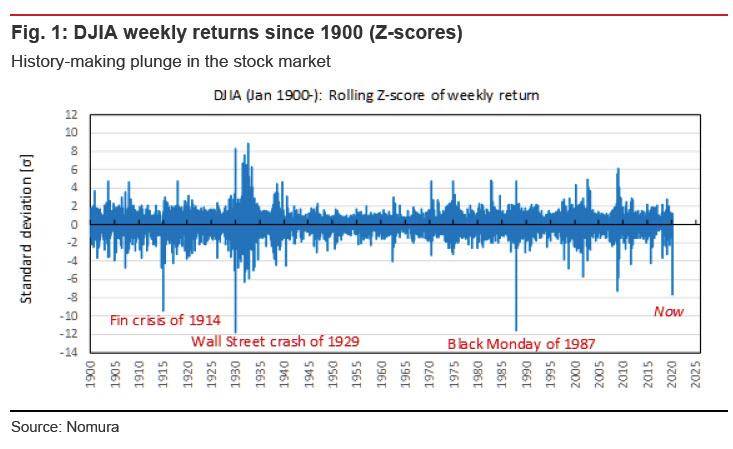
The plunge in US equities yesterday (12 March) pushed weekly returns down to 7.7 standard deviations below the norm. In statistical science, the odds of a greater-than seven-sigma event of this kind are astronomical to the point of being comical (about one such event every 160 billion years).
Setting aside legitimate quibbles over the statistical significance of this, we can say with confidence that we are witnessing a history-making market disaster in real-time.
Looking back at the performance of the DJIA since 1900, market shocks have exceeded the current rout in magnitude on only three occasions: in 1914 (when a growing financial crisis caused trading in US equities to be halted), in 1929 (the historic market crash that led to the Great Depression), and in 1987 (the Black Monday event).
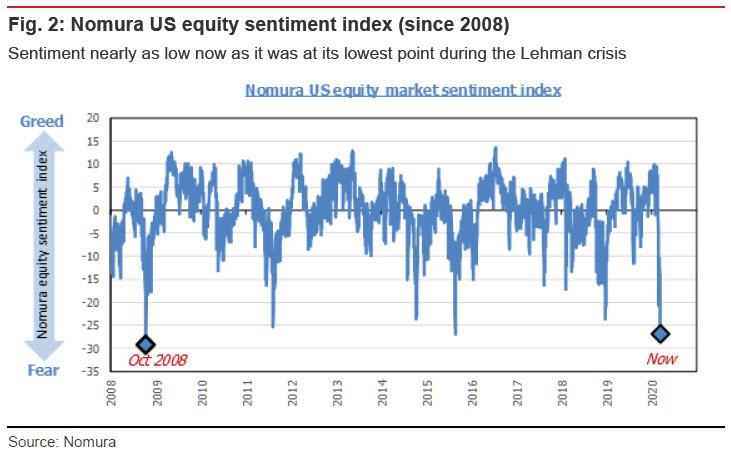
US stock market sentiment has also seen a jarringly swift collapse, as equity sentiment has now gone beyond the low point marked during the 2015 renminbi shock. In little more than the blink of an eye, the situation has come to look like the 2008 Lehman Brothers crisis all over again.
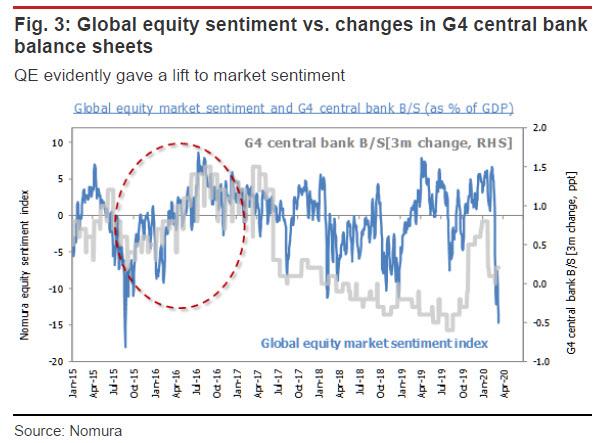
The Fed has resumed its QE-in-all-but-name in response to the financial market meltdown. Many observers have questioned how effective the aid will actually be, given that there seems to be no way to put a conclusive stop to COVID-19. Expanded QE did help lift sentiment in 2015-2016, and therefore think that the Fed can at least help limit the risk of an extreme credit crunch. However, the paralysis in the international circulation of people and goods already being observed will almost inevitably undermine the market.
DM equities worldwide are in bear markets now. Going by our own data analysis, the pace of the present sell-off has broken all norms. When a downshift in the market is characterized by unusually steep declines, the usual driver is an outflow from longer-term investments.
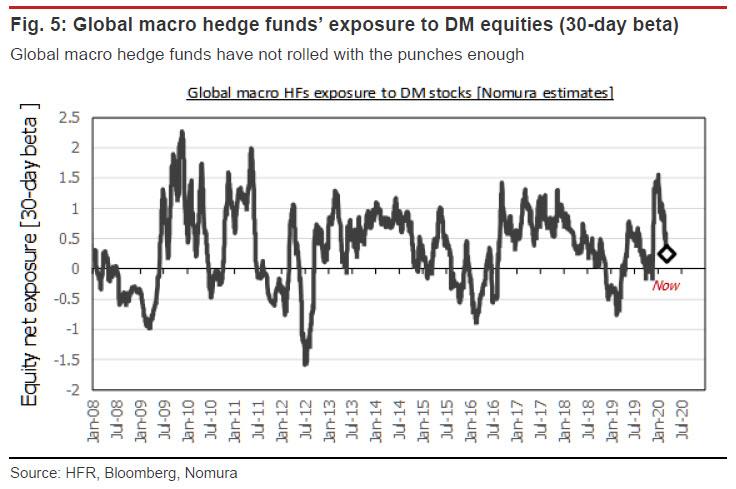
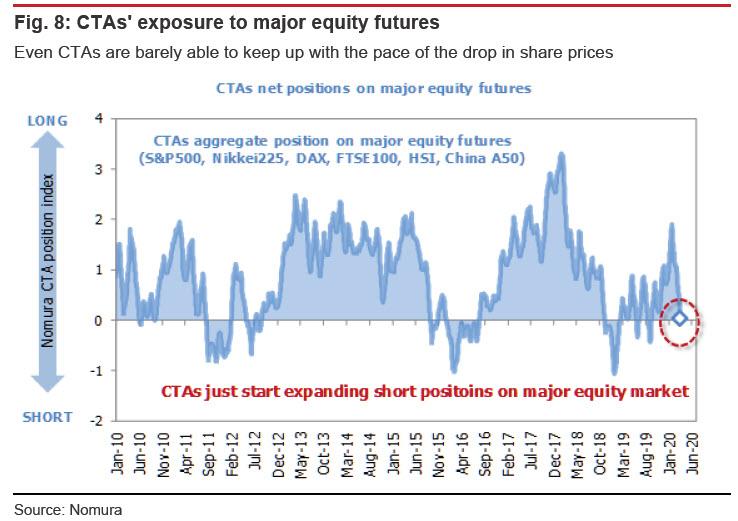
The present market rout is unconventional in that major hedge funds (global macro hedge funds, CTAs) appear to be behind the curve in their selling [ZH: just as Goldman warned this week]. If anything, we see a risk that short-term players may mount an attack on the downside, ramping up their selling in an attempt to push the market down further.
For example, global macro hedge funds’ net exposure to DM equities (estimated from 30- day rolling beta) is still currently flat or even slightly long. It may be that these investors had been unable to fully imagine a pandemic-driven recession scenario, having no experience in that vein to draw upon. Global macro hedge funds may have taken this week’s abnormal market movements as their cue to simply offload their long positions in DM equities in their entirety.
There is a growing risk that global macro hedge funds, after liquidating their long positions, will proceed to aggressively build up short positions. Global macro hedge funds tend not to make spur-of-the-moment trades, but they do tend to stake out positions that are consistent with the macroeconomic outlook.
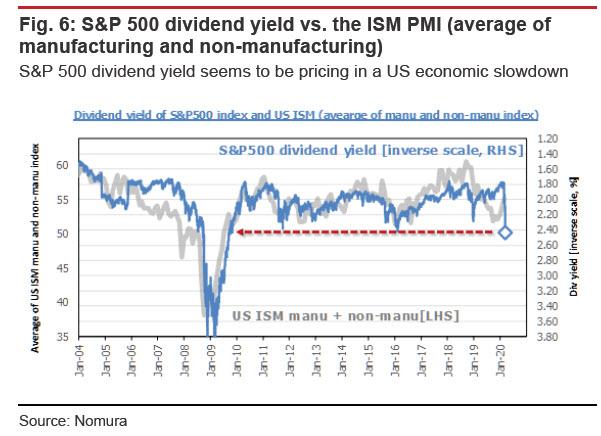
In that respect, the S&P 500 dividend yield appears to already reflect market expectations for a slowdown in the US economy. If the ISM Purchasing Managers Index (average of the readings for manufacturers and non-manufacturers) were to drop to the level recorded around July 2009—as the dividend yield seems to imply—there is a high likelihood that global macro hedge funds would then (with some confidence) start expanding their short positions in pursuit of the market downside.
Similarly, CTAs appear to have failed to fully keep up with the drop in share prices in major countries. CTAs have of course been selling futures to unwind their long positions during this downward move in share prices. But when share prices shift downward abruptly, the short-term surge in volatility can often hinder trend-followers’ ability to participate in short-selling. This is because systematic trend-following strategies tend to build positions that balance: (1) the strength or weakness of trends; and (2) the level of volatility. This means that CTAs often wind up following one step behind when trends shift suddenly.
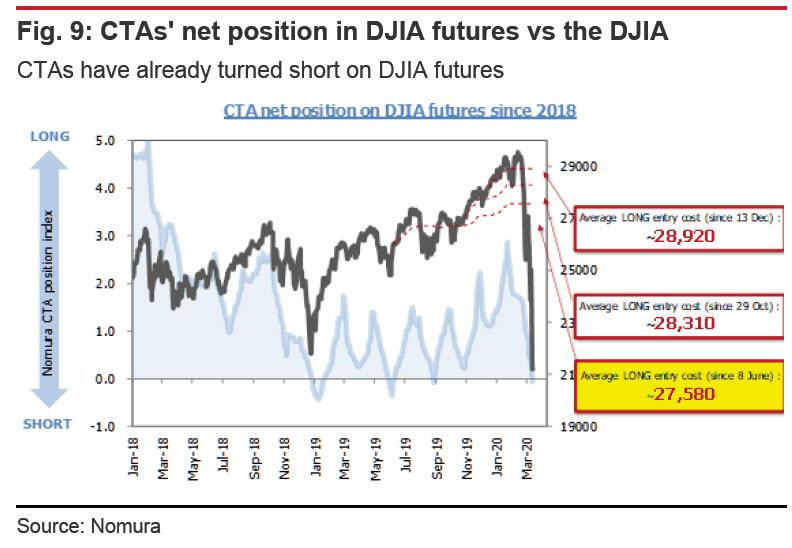
CTAs have turned short on DJIA futures. Because of the rapid pace of the Dow’s drop, CTAs have been able to build sufficient short positions. As they had already preferred short positions with the DJIA below 28,000, CTAs look likely to build short positions rapidly at current share price levels.
It may be, then, that the market has only just begun staring into the abyss.
Tyler Durden
Fri, 03/13/2020 – 20:31
via ZeroHedge News https://ift.tt/2WbPvOY Tyler Durden