“I’ve Never, Ever, Ever Seen Anything Like This Before”
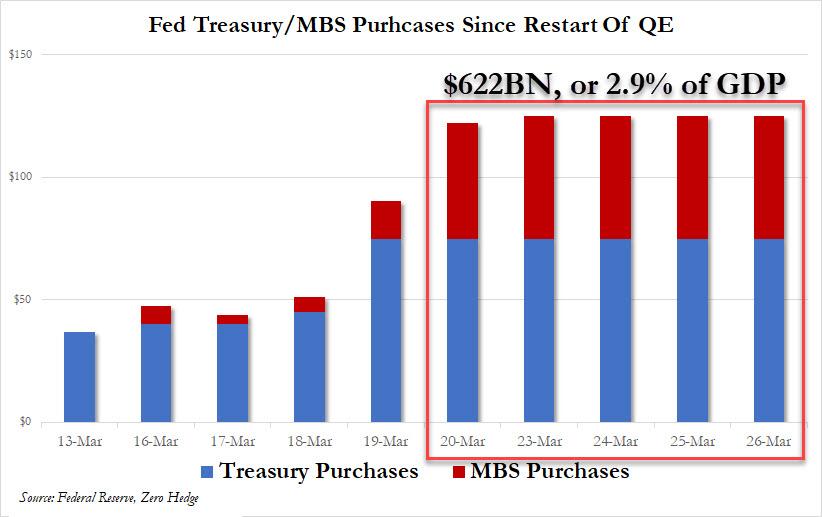
With the Fed buying $622 billion in Treasury and MBS, a staggering 2.9% of US GDP, in just the past five days…
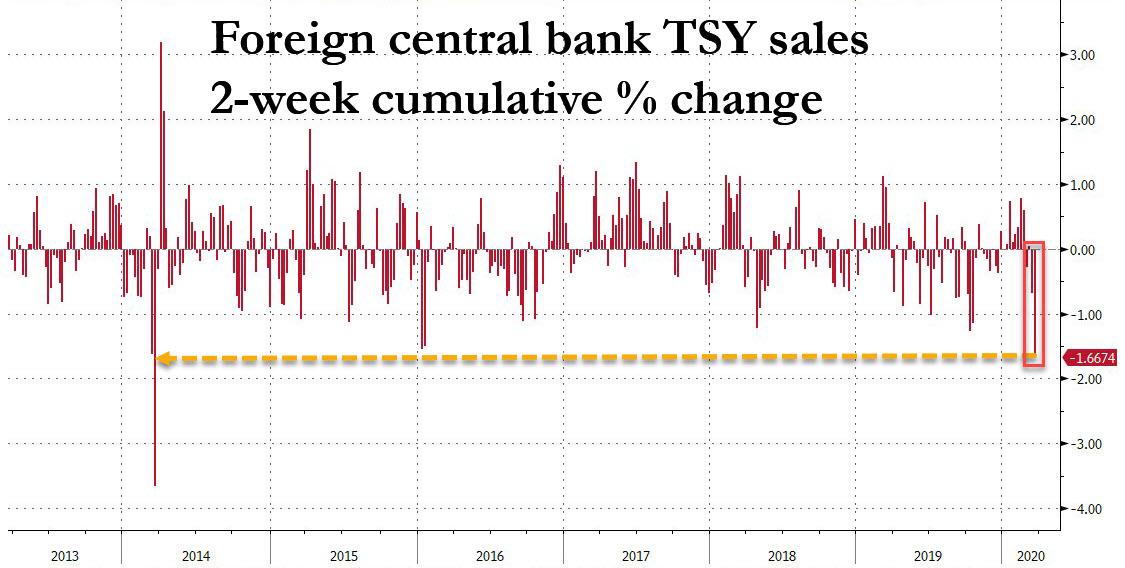
… any debate what to call the current phase of the Fed’s asset monetization – “NOT NOT-QE”, QE4, QE5, or just QEternity – can be laid to rest: because what the Fed is doing is simply Helicopter money, as it unleashes an unprecedented debt – and deficit – monetization program, one which is there to ensure that the trillions in new debt the US Treasury has to issue in the coming year to pay for the $2 (or is that $6) trillion stimulus package find a buyer, which with foreign central banks suddenly dumping US Treasuries…
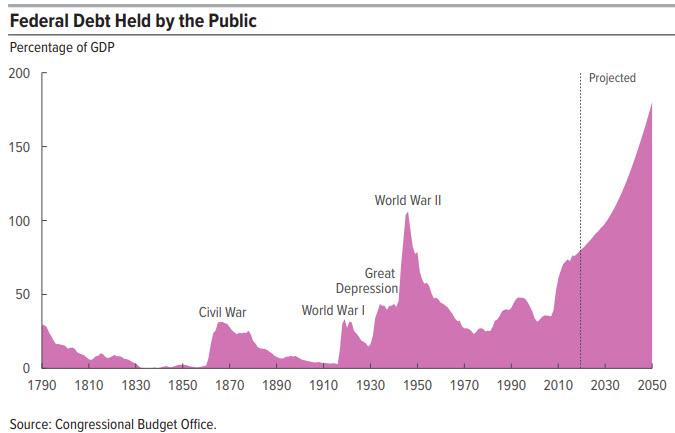
… would otherwise be quite problematic, even if it means the Fed’s balance sheet is going to hit $6 trillion in a few days.
The problem, at least for traders, is that this new regime is something they have never encountered before, because during prior instances of QE, Treasuries were a safe asset. Now, however, with fears that helicopter money will unleash a tsunami of so much debt not even the Fed will be able to contain it resulting in hyperinflation, everything is in flux, especially when it comes to triangulating pricing on the all important 10Y and 30Y Treasury.
Indeed, as Bloomberg writes today, core investor tenets such as what constitutes a safe asset, the value of bonds as a portfolio hedge, and expectations for returns over the next decade are all being thrown out as governments and central banks strive to avert a global depression.
And as the now infamous “Money Printer go Brrr” meme captures so well, underlying the uncertainty is the risk that trillions of dollars in monetary and fiscal stimulus, and even more trillions in debt, “could create an eventual inflation shock that will trigger losses for bondholders.”
Needless to say, traders are shocked as for the first time in over a decade, they actually have to think:
“I’ve never, ever, ever seen anything like this before,” Nader Naeimi, head of dynamic markets at AMP Capital Investors, told Bloomberg.
“You have enormous buyers of debt meeting massive coordinated fiscal stimulus by governments across the globe. For bond investors, you’re caught between a rock and a hard place.”
And while equity investors may be confident that in the long run, hyperinflation results in positive real returns if one sticks with stocks, the Weimar case showed that that is not the case. But that is a topic for another day. For now we will focus on bond traders, who are finding the current money tsunami unlike anything they have seen before.
Indeed, while past quantitative easing programs have led to similar concerns, this emergency response is different because it’s playing out in weeks rather than months and limits on QE bond purchases have quickly been scrapped.
Any hope that the Fed will ease back on the Brrring printer was dashed when Fed Chairman Jerome Powell said Thursday the central bank will maintain its efforts “aggressively and forthrightly” saying in an interview on NBC’s “Today” show that the Fed will not “run out of ammunition” after promising unlimited bond purchases. His comments came hours after the European Central Bank scrapped most of the bond-buying limits in its own program.
The problem is that while this type of policy dominates markets, fundamental analysis scrambling to calculate discount rates and/or debt in the system fails, and “strategic thinking is stymied and some prized investment tools appear to be defunct”, said Ronald van Steenweghen of Degroof Petercam Asset Management.
“Valuation models, correlation, mean reversion and other things we rely on fail in these circumstances,” said the Brussels-based money manager. Oh and as an added bonus, “Liquidity is also very poor so it is difficult to be super-agile.”
The irony: the more securities the Fed soaks up, be they Treasuries, MBS, Corporate bonds, ETFs or stocks, the worse the liquidity will get, as the BOJ is finding out the hard way, as virtually nobody wants to sell their bonds to the central bank.
Another irony: normally the prospect of a multi-trillion-dollar government spending surge globally ought to send borrowing costs soaring. But central bank purchases are now reshaping rates markets – emulating the Bank of Japan’s yield-curve control policy starting in 2016 – and quashing these latest volatility spikes.
In effect, the Fed’s takeover of bond markets (and soon all capital markets), means that any signaling function fixed income securities have historically conveyed, is now gone, probably for ever.
“Investors shouldn’t expect to see much more than moderately steep yield curves, since the Fed and its peers don’t want higher benchmark borrowing costs to undermine their stimulus,” said Blackrock strategist Scott Thiel. “That would be detrimental to financial conditions and to the ability for the stimulus to feed through to the economy. So the short answer is, it’s yield-curve control.”
Said otherwise, pretty soon the entire yield curve will be completely meaningless when evaluating such critical for the economy conditions as the price of money or projected inflation. They will be, simply said, whatever the Fed decides.
And with the yield curve no longer telegraphing any inflationary risk, it is precisely the inflationary imbalances that will build up at an unprecedented pace.
Additionally, when looking further out, Bloomberg notes that money managers need to reassess another assumption that’s become widely held in recent years: that inflation is dead. Van Steenweghen says he’s interested in inflation-linked bonds, though timing a foray into that market is “tricky.”
Naeimi also said he expects that the coordination by central banks and governments will spike inflation at some stage. “It all adds to the volatility of holding bonds,” he said. But for the time being, he’s range-trading Australian bonds — buying when 10-year yields hit 1.5%, and selling at 0.6%.
That’s right: government bonds have become a daytrader’s darling. Whatever can possibly go wrong.
But the biggest fear – one we have warned about since 2009 – is that helicopter money, which was always the inevitable outcome of QE, will lead to hyperinflation, and the collapse of both the US Dollar, and the fiat system, of which it is the reserve currency. Bloomberg agrees:
Many market veterans agree that faster inflation may return in a recovery awash with stimulus that central banks and governments may find tough to withdraw. A reassessment of consumer-price expectations would be a major setback for expensive risk-free bonds, especially those with the longest maturities, which are most vulnerable to inflation eroding their value over time.
Of course, at the moment that’s hard to envisage, with market-implied inflation barely at 1% over the next decade, but as noted above, at a certain point the bond market no longer produces any signal, just central bank noise, especially when, as Bloomberg puts it, “central bank balance sheets are set to explode further into unchartered territory.” Quick note to the Bloomberg editors: it is “uncharted”, although you will have plenty of opportunity to learn this in the coming months.
Alas, none of this provides any comfort to bond traders who no longer have any idea how to trade in this new “helicopter normal“, and thus another core conviction is being revised: the efficacy of U.S. Treasuries as a safe haven and portfolio hedge.
Mark Holman, chief executive and founding partner of TwentyFour Asset Management in London, started questioning that when the 10-year benchmark hit its historic low early this month.
“Will government bonds play the same role in your portfolio going forward as they have in the past?” he said. “To me the answer is no they don’t — I’d rather own cash.”
For now, Mark is turning to high-quality corporate credit for low-risk income, particularly in the longer maturity bonds gradually rallying back from a plunge, especially since they are now also purchased by the Fed. He sees no chance of central banks escaping the zero-bound’s gravitational pull in the foreseeable future. “What we do know is we’re going to have zero rates around the world for another decade, and we’re going to have the need for income for another decade,” he said.
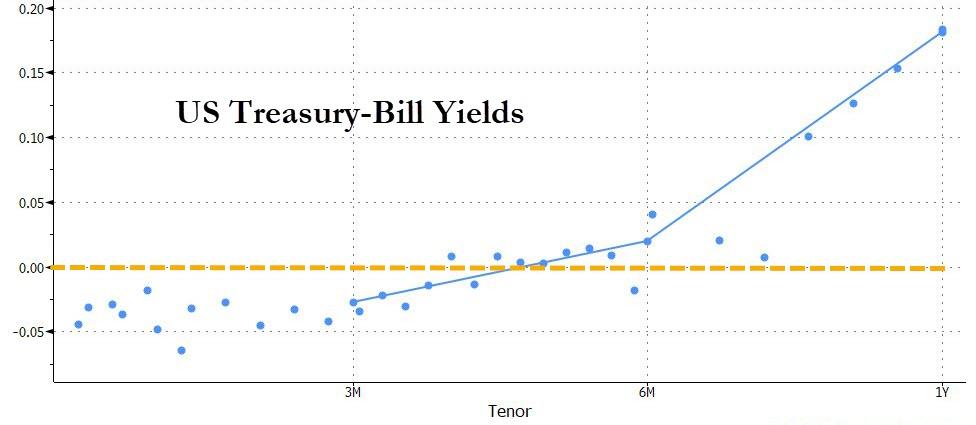
Other investors agree that cash is the only solution, which is why T-Bills – widely seen as cash equivalents – are now trading with negative yields for 3 months and over.
Yet others rush into the safety of gold… if they can find it. At least check, physical gold was trading with a 10% premium to paper gold and rising fast.
Ultimately, as Bloomberg concludes, investors will have to find their bearings “in a crisis without recent historical parallel.”
“It’s very hard to look at this in a historical context and then apply an investment framework around it,” said BlackRock’s Thiel. “The most applicable period is right before America entered WW2, when you had gigantic stimulus to spur the war effort. I mean, Ford made bombers in WW2 and now they’re making ventilators in 2020.”
Tyler Durden
Thu, 03/26/2020 – 15:30
via ZeroHedge News https://ift.tt/2vPSjq3 Tyler Durden