Texas’ Power Grid “Could Be At Risk” Ahead Of Cold Blast
The primary grid operator for Texas, the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT), is preparing for another round of bitterly cold weather that may disrupt natural gas power plants.
National Weather Service (NWS) anticipates temperatures across parts of the Lone Star State to plunge Thursday and affect natgas flows to electricity generators.
The second round of cold air comes as the first blast of arctic air paralyzed several gas wells, processing plants, and other equipment to move natgas to electricity generators. As a result, about 10% of natgas production went offline for 48 hours. It was the most significant disruption to the grid since the state’s infamous February 2021 near power grid collapse.
On Thursday, temperatures in Midland, Texas, the Permian Basin oil and gas field location, will be around 18 degrees Fahrenheit, which is 15 degrees below average for this time of year.
“Gas wells are particularly susceptible to so-called freeze-offs because of the high volumes of subterranean water that typically flow out of the ground alongside the fuel. Wind installations also can be knocked offline by intense cold while overcast weather and snow disrupt solar-power output,” Bloomberg said.
“It is important to remember, however, as we have consistently stated, that some variation in production occurs with sudden temperature changes -– these are field operations, not controlled factory settings,” Todd Staples, president of the Texas Oil and Gas Association, said in a statement.
Ahead of Thursday, ERCOT filed a report with state regulators that outlined most of its power-generating units comply with new winterization rules following last year’s power grid problems. The grid operator found ten generators out of the 302 inspected didn’t meet the new requirements to survive a winter storm. The generators susceptible to volatile weather represent a total capacity of 532 megawatts or about .4% of ERCOT’s generation.
“The Texas electric grid is more prepared for winter operations than ever before,” Brad Jones, ERCOT’s interim CEO, said in a statement. The units examined by ERCOT contribute about 85% of the power to the state’s grid.
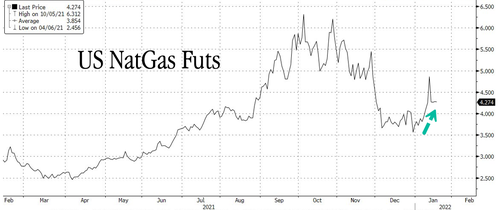
While Texas and much of the US brace for a colder back half of January, natgas prices linked to Henry Hub have been on a tear in recent weeks on the prospects of colder weather and snowstorms in the eastern half of the US.
“Winter is the key catalyst for gas, with the outlook in-line with our reserved view. Yet weather is volatile and softer output from well freeze-offs may help. Benchmarks in the $4 range are consistent with our view,” Bloomberg Intelligence analysts Vincent Piazza and Evan Lee said.
“If we experience another severe winter storm before operators have weatherized their equipment, the grid could be at risk again,” said Virginia Palacios, executive director of watchdog group Commission Shift.
Tyler Durden
Wed, 01/19/2022 – 07:59
via ZeroHedge News https://ift.tt/34TWKkO Tyler Durden