Japan Proposes Dumping Radioactive Waste Into Pacific As Storage Space Dwindles
As the decade comes to an end, the future of nuclear power in the west remains in doubt. Almost nine years ago, a powerful underwater earthquake triggered a 15-meter tsunami that disabled the power supply and cooling at three of the reactors at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant.
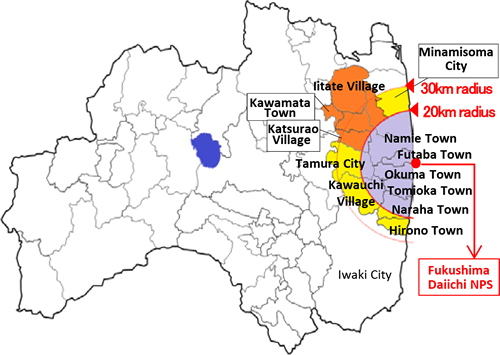
The accident caused the nuclear cores of all three damaged reactors to melt down, prompting the government to issue evacuation orders for all people living within a 30 kilometer radius of the damaged reactors, a group that included roughly 100,000 people.
And the evacuation zone:
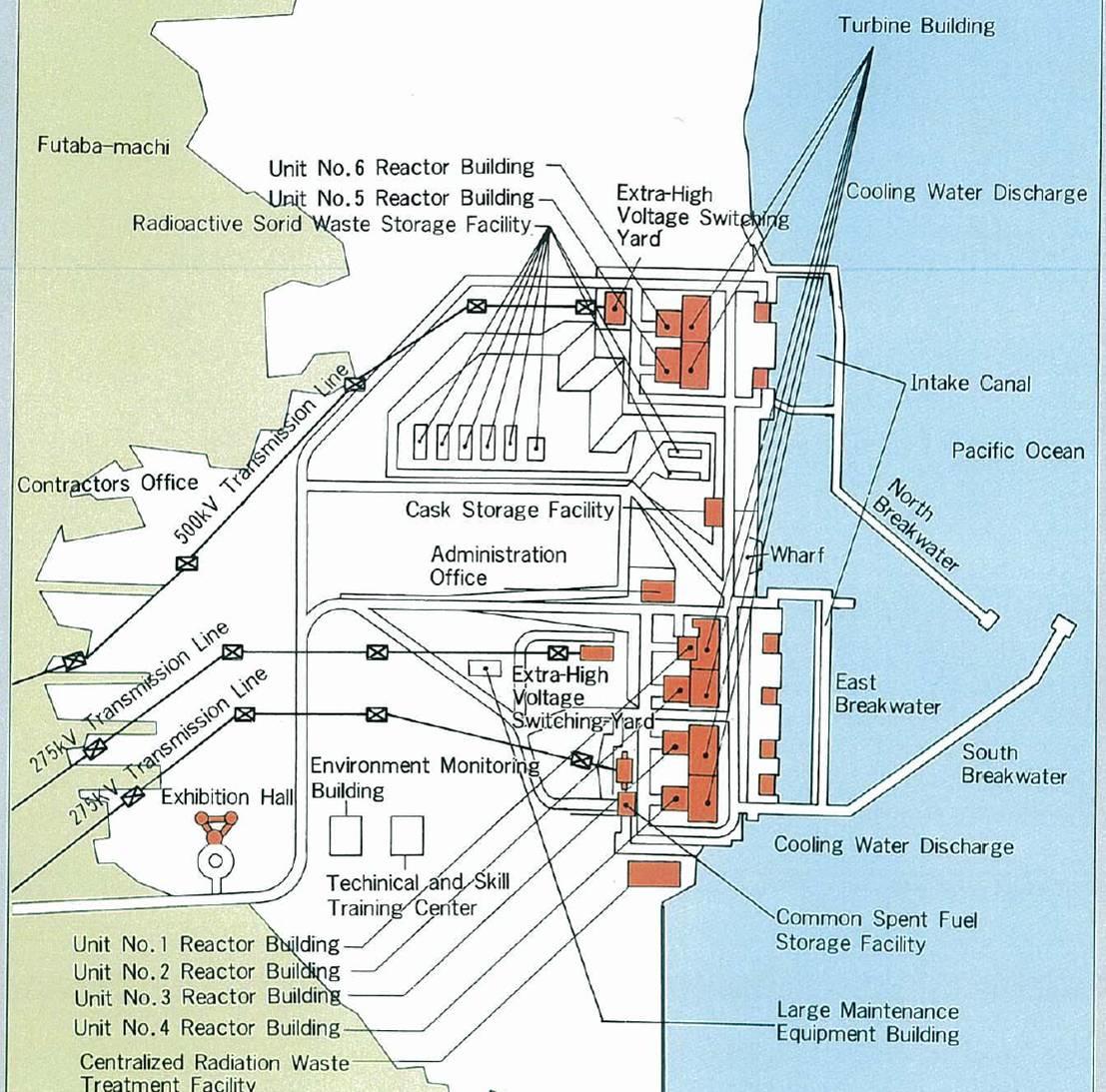
Now, the Epoch Times reports that Japan’s Economy and Industry Ministry has proposed that TEPCO gradually release, or allow to evaporate, massive amounts of treated but still radioactive water being stored at the power plant. TEPCO, or the Tokyo Electric Power Co, is the owner of the Fukushima plant, and is also responsible for leading the clean-up of the damaged reactors.
But as regulators have stepped in to try and guide TEPCO as it struggles to dispose of all the contaminated water, one ministry has offered a proposal that is almost guaranteed to anger the fishermen who have resisted all of TEPCO’s other plans for dumping the contaminated water.
In its Dec. 23 proposal, the ministry suggested a “controlled release” of the contaminated water into the Pacific. Offering another option, the ministry also suggested allowing the water to evaporate, or a combination of the two methods.
The government is stepping up the pressure on TEPCO to do something as Fukushima’s ‘radioactive water crisis’ worsens. The problem is that TEPCO is running out of room to store the contaminated water.
But the ministry insisted that the controlled release of the contaminated water into the sea would be the best option because it would “stably dilute and disperse” the water from the plant, while also allowing the government and TEPCO to more easily monitor the operation.
And as we have reported, the Japanese fishing industry isn’t the only party that objects to the government’s plan. South Korea has also complained to the IAEA about TEPCO’s plans to dump the radioactive water.
The project is expected to take years to fully dispose of the water.
Still, the fishermen are bound to be skeptical because of one radioactive element that TEPCO has been unable to remove from the contaminated water: It’s called tritium.
Fukushima fishermen and the National Federation of Fisheries Co-operative Associations have strongly opposed past suggestions by government officials that the water be released to the sea, warning of an “immeasurable impact on the future of the Japanese fishing industry,” with local fishermen still unable to resume full operations after the nuclear plant accident.
The water has been treated, and the plant operator, Tokyo Electric Power Co., states that all 62 radioactive elements it contains can be removed to levels not harmful to humans except for tritium. There is no established method to fully separate tritium from water, but scientists say it isn’t a problem in small amounts. Most of the water stored at the plant still contains other radioactive elements including cancer-causing cesium and strontium and needs further treatment.
Tritium is routinely found in nuclear explosions and other nuclear accidents, including the meltdown at Three-Mile Island back in 1979. But experts at the IAEA recommend that the controlled release of the tritium-laced water at Fukushima into the sea is probably the best option for handling the situation – even if the Japanese decide to wait until after the Summer Olympics in 2022.
The ministry noted that tritium has been routinely released from nuclear plants around the world, including Fukushima before the accident. Evaporation has been a tested and proven method following the 1979 core meltdown at Three Mile Island nuclear plant in the United States, where it took two years to get rid of 8,700 tons of tritium-contaminated water.
TEPCO says it is currently storing more than 1 million tons of radioactive water and only has space to hold up to 1.37 million tons, or until the summer of 2022, raising speculation that the water may be released after next summer’s Tokyo Olympics. TEPCO and experts say the tanks get in the way of ongoing decommissioning work and that space needs to be freed up to store removed debris and other radioactive materials. The tanks also could spill in a major earthquake, tsunami, or flood.
Experts, including those at the International Atomic Energy Agency who have inspected the Fukushima plant, have repeatedly supported the controlled release of the water into the sea as the only realistic option.
On Dec. 22, some experts on the panel called for more attention to be given to the impact on the local community, which already has seen its image harmed by accidental leaks and the potential release of water.
“A release to the sea is technologically a realistic option, but its social impact would be huge,” said Naoya Sekiya, a University of Tokyo sociologist and an expert on disasters and social impact.
Other possible strategies for disposing of the contaminated water have included injecting the water deep into the Earth’s crust. Another strategy, which called for storing the nuclear waste in large industrial tanks outside the plant, was ruled out because of fears that leaks in the tanks could contaminate some of Japan’s most important fishing waters.
Tyler Durden
Tue, 12/24/2019 – 23:30
via ZeroHedge News https://ift.tt/2ZmFeil Tyler Durden