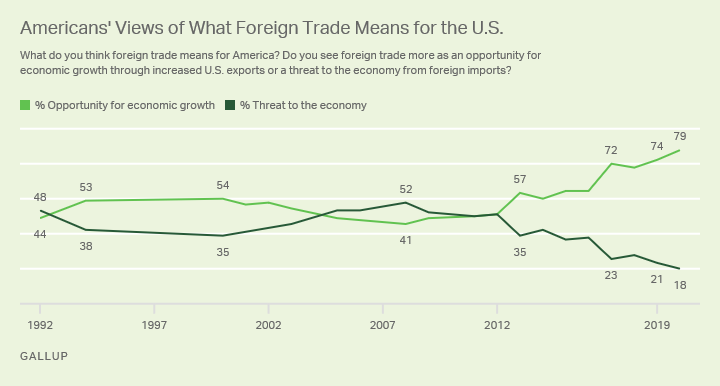
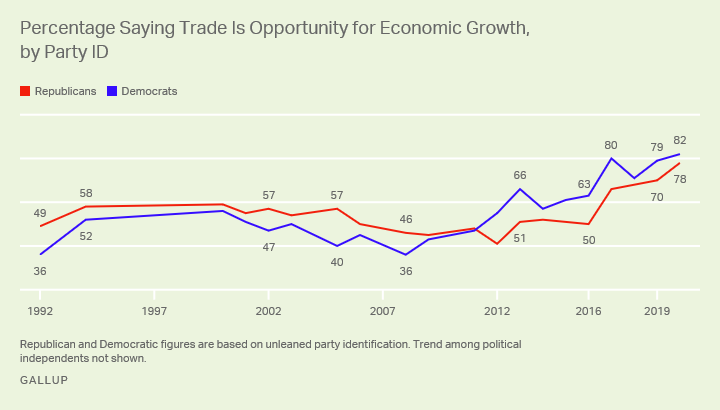
Greece’s Migrant Crisis: “A Powder Keg Ready To Explode”
Authored by Soeren Kern via The Gatestone Institute,
A plan by the Greek government to build new migrant camps on five Aegean islands has sparked violent opposition from local residents, who fear that the facilities will encourage yet more mass migration from Africa, Asia and the Middle East.
The government says that the new camps, expected to be operational by July 2020, are needed to alleviate overcrowding at other locations that have been the focus of international criticism. Local residents counter that the migrants should be transferred to mainland Greece.
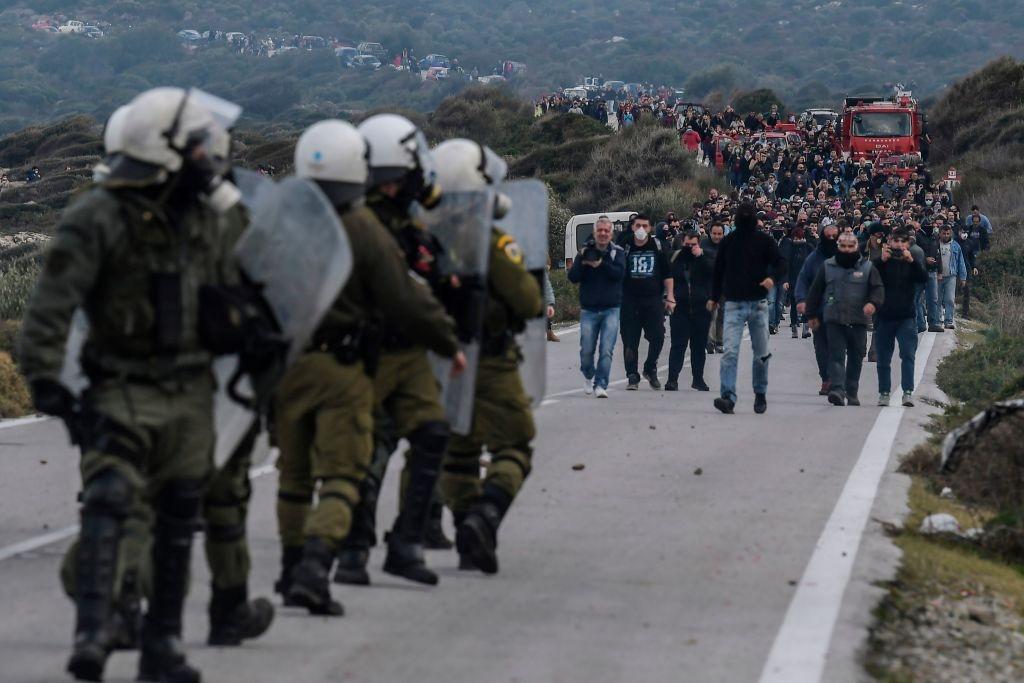
On February 25, more than 500 locals prevented construction workers from accessing the site of a proposed new migrant camp at Karava Mantamadou on Lesbos. Riot police used tear gas and stun grenades to disperse the crowds.
Similar clashes occurred on Chios, a large Greek island located less than 20 kilometers from Turkey, from where tens of thousands of migrants depart each year in hopes of eventually reaching mainland Europe.
The new site on Lesbos will be a so-called closed camp that tightly controls access and will replace the current open-access camp at Moria. The closed camps will allow migrants to go out during the day but will require them to be locked in at night. The objective is to control their movements and prevent them from escaping to the mainland.
In addition to Lesbos, Greek authorities plan to build closed facilities on the islands of Chios, Kos, Leros and Samos. The islands are all close to Turkey.
The camp at Moria — a sprawling facility built for no more than 3,000 migrants but which is now accommodating at least 20,000, approximately one-third of whom are under the age of 18 — has attracted widespread international criticism for its squalid living conditions.
A spokesperson for Doctors Without Borders (Médecins Sans Frontières, MSF), Sophie McCann, explained:
“They are living in squalid, medieval-like conditions… with barely any access to basic services, including clean and hot water, electricity, sanitation and healthcare. On a daily basis our medical teams are treating the consequential deterioration of health and wellbeing.”
In 2016, Greek authorities, with backing from the EU, introduced a so-called containment policy aimed at deterring migrants from crossing to Greece from Turkey. The policy requires migrants to remain on the islands — with no hope of reaching the Greek mainland — until their asylum requests are processed. With a backlog of tens of thousands of applicants, the asylum system has come to a standstill. Approximately 40,000 migrants are effectively trapped on the islands.
The containment policy has angered local residents, who complain that migrants are responsible for a spike in crime.
“People have seen their properties destroyed, their sheep and goats have been slaughtered, their homes broken into,” said Nikos Trakellis, a community leader in Moria.
“A few years back, when there were 5,000 migrants on the island, things seemed bad enough. Now there’s a sense that the situation has really got out of hand.”
In October 2019, the Greek government announced a plan to transfer 20,000 migrants from the islands to the mainland. A subsequent surge in new migrant arrivals from Turkey, however, has left the migrant camps on the islands as overcrowded as ever.
Greek authorities say that they are doing their best to satisfy locals, migrants and human rights groups. “The government is making an effort to change something, to implement a plan,” a government official told the Reuters news agency. “If we don’t construct new facilities, living conditions won’t improve.”
North Aegean Regional Governor Kostas Moutzouris, who opposes the government’s plan to build permanent migrant camps on the islands, described the situation on Lesbos as a “powder keg ready to explode.” He added: “It’s crucial that a state of emergency is called.” He also warned:
“I fear for the safety of our people, the residents of Lesbos. For the situation to change, many refugees have to be transferred to the mainland and new arrivals from Turkey must be stopped. If not, we are doomed.”
Government spokesperson Stelios Petsas, who described the existing facilities as “public health bombs,” said:
“We are asking the local communities to understand that these closed facilities will benefit the country and their communities. There’s a trust deficit right now that has been cultivated over previous years, and this needs to be restored. We will build these closed centers but also close the existing open ones. That is the government’s promise.
“The new camps will make it much easier to speed up the asylum process so that those who are entitled to asylum can be transferred west and those who are not can be returned to Turkey.”
Greece’s center-right government, led by Greek Prime Minister Kyriakos Mitsotakis, who took office after parliamentary elections in July 2019, has taken a more hardline approach toward migration than did the previous left-wing government led by Alexis Tsipras:
-
July 2019. The new government revoked access to public health care for asylum seekers and undocumented migrants arriving in Greece.
-
September 2019. The government raised the criteria for both the application and approval of asylum status applications. It also vowed to strengthen border security and return 10,000 illegal migrants back to Turkey by the end of 2020.
-
October 2019. The Greek parliament passed a new asylum law, which introduced sweeping changes to the national asylum system, including cutting options for appeal and facilitating the deportation of failed asylum seekers.
-
November 2019. The government said that it would tighten controls at Greece’s borders and clear bottlenecks in asylum vetting procedures.
-
January 2020. The government announced the construction of a floating fence to deter migrants arriving by sea. The 2.7-kilometer (1.7 mile) barrier will be set up off coast of Lesbos. It will rise 50 centimeters above sea level and have lights that will make it visible at night. If the barrier is effective at reducing migration, it could be extended to 15 kilometers or more.
-
February 2020. The Greek parliament approved a law to regulate all non-governmental organizations (NGOs) dealing with migration issues. The objective is to ensure that NGOs are not profiting from mass migration “in a faulty and parasitic manner.”
Mitsotakis recently said that, unlike under the previous government, Greece is no longer open to anyone who wants to come:
“Welcome in Greece are only those we choose. Those who are not welcome will be returned. We will permanently shut the door to illegal human traffickers, to those who want to enter even though they are not entitled to asylum.”
Since 2015, more than a million migrants from Africa, Asia and the Middle East have entered the European Union through Greece.
A March 2016 agreement between the EU and Turkey reduced the flow, but the number of arrivals resurged in 2019, after Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan and other members of his government threatened to flood Europe with Muslim migrants.
Greek officials have said that Erdoğan personally controls the migration flows to Greece and turns them on and off to extract more money and other political concessions from the European Union.
Greek Immigration Minister Giorgos Koumoutsakos noted that when Turkey “keeps repeating that we’re going to open the floodgates, what migrants do is they move closer to the floodgates waiting for them to open.” He added:
“Europe cannot act under threats or blackmail. As Europeans should understand the situation that the Turks are faced with, Ankara should on its part realize that this is not the way to deal with Europe.”
In 2019, approximately 60,000 migrants — an average of 164 per day — reached Greece, according to UNHCR, the UN refugee agency. Nearly 80% arrived on Chios, Lesbos and Samos.
The trend continues: More than 6,000 migrants — an average of 133 per day — reached Greece during the first six weeks of 2020, according to the UNHCR. The top countries of origin: Afghanistan (50%); Syria (21%); Congo (6%) and Iraq (3.5%).
Recent fighting in Idlib, a war-torn province in northwestern Syria, has uprooted nearly one million people — most of them women and children — who have sought sanctuary near the Turkish border.
Turkey, which currently hosts nearly four million Syrian refugees, has said it cannot handle a new influx. It has repeatedly threatened to re-open the floodgates of mass migration to Europe.
Tyler Durden
Sat, 02/29/2020 – 07:00
via ZeroHedge News https://ift.tt/32GEA10 Tyler Durden