Authored by Robert Scheer via TruthDig.com,
Was it conspiracy or idiocy that led to the failure of U.S. intelligence agencies to detect and prevent the Sept. 11, 2001, attacks on the World Trade Center and Pentagon headquarters? That’s one of the questions at the heart of “The Watchdogs Didn’t Bark: The CIA, NSA, and the Crimes of the War on Terror,” by John Duffy and Ray Nowosielski. In their careful and thorough investigation of the events leading up to the attacks, the authors uncover a story about the Central Intelligence Agency’s neglect, possible criminal activities and a cover-up that may have allowed al-Qaida to carry out its plans uninhibited by government officials.

In the latest installment of “Scheer Intelligence,” the journalists tell Truthdig Editor in Chief Robert Scheer how an interview with Richard Clarke, the counterterror adviser to Presidents Bill Clinton and George W. Bush, led them to a jaw-dropping revelation regarding two hijackers involved in the infamous attacks. As it turns out, Khalid Muhammad Abdallah al-Mihdhar and Nawaf al-Hazmi, two men linked to al-Qaida, were staying at an FBI informant’s home in San Diego in 2000, and they were being tracked by the National Security Agency. Despite knowledge of the men’s ties to the terrorist organization responsible for 9/11, neither was investigated by the FBI. Clarke and others believe that this may have had to do with a CIA attempt to turn the two men into agency informants.
“When we sat down with Clarke … he told us he couldn’t see any other explanation but that there was an op [and] that it never made it to the White House because it would have had to go through him,” says Nowosielski.
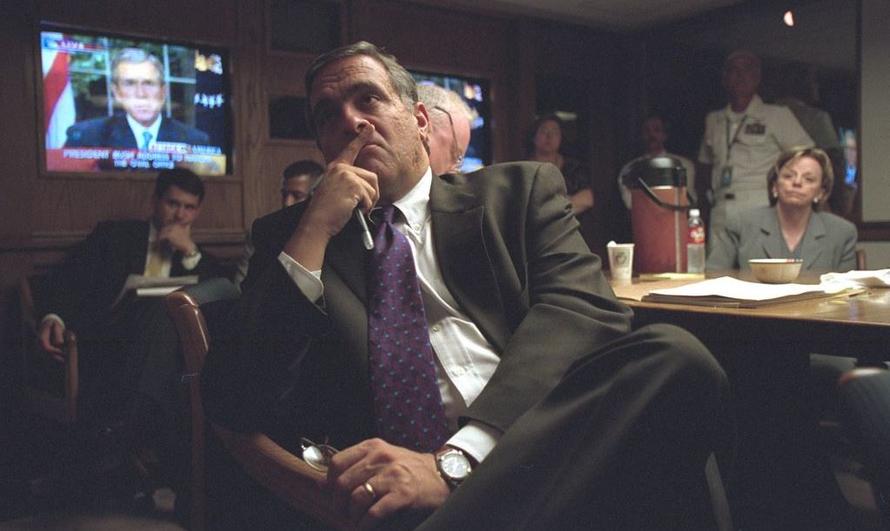
“And his friend [then CIA Director] George Tenet was responsible for malfeasance and misfeasance in the runup to 9/11.”
Once the plans for the 9/11 attack must have become clear to the CIA, why didn’t the agency prevent it from taking place? Duffy and Nowosielski come to the simple, shocking conclusion that because the CIA is prohibited from operating on U.S. soil, those involved in the operation chose to avoid prosecution rather than come clean.
In a well-documented case study that touches senior government officials, including current special counsel Robert Mueller and other high-level individuals, crucial questions arise about who is responsible for allowing “a plot that resulted in 3,000 murders” and led to ongoing U.S. military entanglements in the Middle East to move forward.

However, our country’s recent crimes and the people behind them, including President Bush, are currently being “whitewashed” by our national obsession with Donald Trump, the authors warn.
“All the crimes of the war on terror, the torture, Abu Ghraib, it’s all just gone—the unnecessary invasion of the war in Iraq, it’s all just sort of under the rug now because of Trump,” Duffy says.
Listen to their discussion to learn more about the stunning investigation into the tragedy that changed the course of our nation’s history and the Americans who could have thwarted the attacks but decided to cover their own backs instead. You can also read a transcript of the interview below the media player.
RS: Hi, this is Robert Scheer with another edition of “Scheer Intelligence,” where the intelligence comes from my guests. And the title is really appropriate for the book we’re going to talk about today, “The Watchdogs Didn’t Bark: The CIA, NSA, and the Crimes of the War on Terror.” And the authors are John Duffy and Ray Nowosielski. And they are investigative reporters, and the watchdogs here are the people in our intelligence agencies that are supposed to be protecting the nation. And this book cuts very deeply into the unsolved mystery of how 9/11 happened. Why weren’t we better prepared to prevent it? It’s one of the most important events in American history; it certainly has shaped our lives in terms of a surveillance state, our rights and everything else, up to the present. And this book, I think, represents the most exhaustive and well-documented effort to get to the bottom of the whole thing. You’re very careful in what you do and do not assert about 9/11, what we don’t know about it, and particularly the role of George Tenet, who was then head of the CIA, and the role of the CIA in—what is the right word?—obscuring the story, even keeping information from the White House, from the FBI. So give me the gist of the book.
RN: This is Ray. The book is largely about looking at this case study of the failure leading up to 9/11, the people who were involved in that failure, how that came about, and how they were successful, to the present day, in managing to obscure the public from really fully understanding that this was, in the words of one of our sources, really just a handful of people. And the most jarring thing is that they’re still, in some cases, working today in I guess Trump’s CIA. And we sort of document through the second half of the book what damage was done to America because they remained in their positions.
JD: This is John. And intelligence was gathered around the time of the millennium that led people in the Bin Laden unit at the CIA to monitor a meeting in Malaysia that was a gathering of these al-Qaida figures. In monitoring this —
RS: That was in the year 2000, right?
JD: Yes. Right at the outset of the year. In monitoring this meeting, they became aware of the fact that one of the attendees had a multiple-entry visa to the United States. That man’s name was Khalid al-Mihdhar. He would eventually be on the plane that crashed into the Pentagon; he was one of the hijackers. So this starts the whole thing there, the fact that the CIA becomes aware of this information; the Bin Laden unit, counterterror center, and then all the way up to George Tenet are aware of this information. There’s a lot of ins, outs, and what-have-yous about where that information goes, but it ultimately does not go over to the FBI’s counterterror division in New York, much to the protest of the FBI agents who were detailed to the CIA’s Bin Laden unit. And it did not make it to the White House counterterror czar, Richard Clarke, who very much finds this to be, like, the crux of the whole story—the fact that this information was kept from his office for basically a year and eight months, up until the success of the attacks. The crux is there, that they had this information, these guys were coming into the country, they had just left the terror planning summit, and this information was being held close by the Bin Laden unit, by the counterterror center, and by George Tenet. The reason for that is unknown; the speculation that Richard Clarke has was that George Tenet and these people in the Bin Laden unit and counterterror center thought having these al-Qaida people in the United States, they could possibly go through Allied proxies in the Saudi intelligence to try to get close to these guys, monitor them, potentially find out information from them or even try to flip them. That’s Richard Clarke’s speculation as to why this was kept from him for so long. Ultimately, the attack was successful; that they all just did their best to bury all this and, you know, hope no one noticed.
RS: Let me just start off with something that was confusing to me in reading your book. Because the FBI generally comes off looking pretty good in your book, and the real problem is with the CIA, and to a lesser degree, with the NSA. And in the San Diego story, and this is covered in the 9/11 Commission Report and others, the two San Diego guys—they are staying at the home of an FBI informant at first. So when you say the FBI was not informed, weren’t some of these calls actually made from the home of an FBI asset?
RN: It’s interesting when you know, A, that according to our NSA sources they were able to be pinged every time that Mihdhar and Hazmi, the two hijackers, called from that house that you mentioned in San Diego, back to Yemen. That somebody in the NSA was getting an alert as that was happening each time, and was aware of those connections. But that the house that was being used for the phone call was that of an FBI informant, Abdussattar Shaikh. And Abdussattar was somebody the FBI recruited who was inside a popular mosque in San Diego, and who they thought might be able to feed them warnings of anybody who might be a radical Muslim terrorist. And Abdussattar claims that he simply missed the warning signs of the two tenants that he had in his home. I mean, it’s kind of interesting. He’s also, he’s not just an FBI informant, he’s also a Saudi, which kind of points to Richard Clarke’s conjecture, which he first laid out to us when we sat down in his office in 2009. And that was that once the CIA monitored the meeting in Malaysia, knew that these two guys were connected to Bin Laden and were of interest, and saw that they were heading to the United States, in Clarke’s words, they might well have thought that the best way to try to recruit these guys to feed information was not to send a blue-eyed, blonde-haired, American CIA agent to go to meet them. But, instead, to use our partners in Saudi Arabia and Saudi intelligence—which George Tenet, the head of the CIA, happened to be very close with—to try to recruit them. So I actually focus more on the fact that this guy was introduced to this house by a gentleman who’s been determined to be a Saudi agent, a guy named Omar al-Bayoumi, and that this guy then was perhaps working dually for Saudi intel and as an FBI asset. And everyone sort of focuses on, oh, Abdussattar Shaikh was an FBI asset, so that seems to put blame at the feet of the FBI. Could be; could be, but I would also focus on that Saudi angle, because it recurs so often.
RS: Well, it also goes to the question of the efficiency of the surveillance society. Because after all, these phone calls could be intercepted. You know, they did; they could follow this trail. And phone calls are being made back to a suspect residence in Yemen and so forth, from the home of an FBI recruit. And I’m just wondering, there’s been a lot of discussion, some of the people that you quote in your book have made this point—you collect this haystack of information that doesn’t lead you to the needle in the haystack. And so here these phone calls were, clearly could be intercepted. They didn’t require any special act of Congress or anything else. This was not a case of their arms being tied, the intelligence agencies. But they’re not even looking at their own data. Isn’t that the takeaway from the first part of this story? These guys are acting suspiciously in San Diego, they have a suspicious background, they’ve participated in a suspicious conference, they’re staying at the home of an FBI informant, and they’re making calls that would basically outline what was going to happen in this disastrous attack—and no one noticed. Or the ones who noticed didn’t tell other people.
JD: I think what is likely to have happened there is, so those calls were going back, and I think it was about seven or eight calls. And Khalid al-Mihdhar’s wife still lived at that house, and he was calling her from San Diego. So I don’t think any deep operational details were being discussed in those calls, but that doesn’t really matter; the fact that they’re calling that home from America is a big deal. And how that would work at the NSA is there’s someone who is tasked all day with basically monitoring the electronic signals going into and out of this house in Yemen, and when they see this coming in from the United States, that should ring a really big alarm bell. Now, that person working that desk would have to seek approval from the chop chain, which are these NSA managers. In order for anything to happen with that information, it has to get passed up and then brought to a FISA court, brought to the FBI. And if these managers within the NSA basically say, don’t worry about it, sit on it, just collect it, sit on it—and if they don’t allow any action, then there will be no action. And it’s just going to stay housed right there, in that particular data stovepipe at the NSA. If Richard Clarke’s speculation is true, that there was this attempt to recruit these guys in the U.S. with Saudi proxies, part of that plan would have been George Tenet speaking to someone at the NSA, or one of George Tenet’s people speaking to someone at the NSA. Basically saying, hey, before you go out getting any FISA warrants or chasing anything down regarding this specific house, come to us first. So if there is some operation going on, it would stand to reason that part of that operation would be not allowing these pings at this particular desk to turn into any action.
RS: For people listening, let me make clear, this is an incredibly detailed, researched book, which relies very heavily on intelligence veterans. No one less so than Richard Clarke, who’s come up so far; another is former colonel Larry Wilkerson, obviously a key person. And what is very dramatic in your book is, where your story really comes to life for you guys as journalists, is when Richard Clarke—you say you go in there to interview him, and you tell your crew, put the sound on as we go in. And you go in, and you think you’re going to have to ask a lot of questions to get—and for people who don’t know, Richard Clarke ever since the early ’70s was a major figure in the intelligence community. And at this point, when you’re talking to him, he’s been around the block, he’s seen everything. And he was a close friend of George Tenet, who was head of the CIA; they considered themselves allies. And you’re going in to get this interview, and you think you’re going to have to weasel information out of him. And he just hits you over the head with an assertion that, really, is the thrust of this book. So why don’t you take us to that moment?
RN: What we discovered on the day that we walked into Richard Clarke’s conference room was that he’d been ready for probably about a year to talk about this, and no major journalists had called him up to ask him about this subject. Nobody had ever asked him. So going back, you know, he started in the Reagan State Department; he worked under George H.W.; Clinton, when these Al Qaeda terrorist attacks began in the early nineties, recognized that there needed to be a new position within his Cabinet, and he called it the counterterror czar, the counterterror adviser. And he created that position for Richard Clarke. As you mentioned, Clarke was close friends with George Tenet, who also was sort of on the National Security Council under Clinton early on, and then got named the head of the CIA in the midst of Clinton’s first term. George W. Bush and company come in, early 2001; as it turned out, nine months ahead of this ticking clock towards 9/11. And Richard Clarke is told that he’s essentially being demoted. He’s still going to be the counterterror advisor, but it’s not a Cabinet-level position. And so now he’s kind of essentially going through the extra layer of Condoleezza Rice. But George Tenet still very much has Bush’s ear. And that’s kind of the back story there; then after, you know, on 9/11 Richard Clarke by nearly all accounts was running the response that morning, on that critical day; he was the top man for counterterror. Over time, he starts to get rubbed the wrong way by the fact that the Bush administration inexplicably is not really terribly still concerned about Al Qaeda after 9/11. But then Clarke leaves, and he writes a bestselling book. And he testifies before the 9/11 commission and becomes the only person to apologize to the families, to admit that there was a failure at all. But cut to a few years down the line, and he releases another book in 2008 that doesn’t become a bestseller. And it’s called “Your Government Failed You.” And it includes a section on Mihdhar and Hazmi that he calls “Straining Credulity,” in which he says that he does not believe in conspiracy theories, but in this one particular case, he’s weighed it every which way and he can’t see another way to explain it but by. But he sort of saved us speculation, and so we saw that part in his book and we thought, well, we’ve been itching—we’d collected enough info by that time, and talked with enough people, that we thought: something happened here with these two hijackers that flew over to the U.S. Something happened when they arrived. And the big question was, if this was an operation by the CIA, did they let Clinton know? Did they then let Bush know when he came in? What was the deal there? And Richard Clarke would be the man in a position to answer that. And so you’re right, that’s where our journey really—that’s where we launched. Because we’d been looking into it for a few years, but when we sat down with Clarke, that was when he told us he couldn’t see any other explanation but that there was an op, that it never made it to the White House because it would have had to go through him. And his friend George Tenet was responsible for malfeasance and misfeasance in the runup to 9/11.
JD: And he also, in part of that description, said that a lot of the CIA reports that would have, any other day, come directly to his computer—when he flicked it on in the morning, it would be right there waiting for him—just on this specific case with these two individuals, he was removed from the chain of information. And so he felt that he was getting minutiae concerning terrorism from around the world in, like, tiny micro-detail on everything except this, and that must have meant he was intentionally pulled out of the chain by someone. And that that would have taken high-level order. And when asked, you know, how high level, he said that it must have come from the director, referring to George Tenet.
RS: So let’s cut to the chase here. There’s an old caution, don’t attribute to conspiracy what can be explained by ordinary stupidity. Or laziness, or incompetence. Is this a case where George Tenet, the admired at that time head of the CIA, was just incompetent, stupid, indifferent? Is there something more at work? Did the CIA welcome such an attack as a boon for the military-industrial complex, as some people allege? What’s going on here? How could this major tragedy event be visited upon the United States, the head of our intelligence agency knows that there are these suspect characters there, and he doesn’t bother to tip off the FBI, let alone the White House? And after all, the FBI is in charge of domestic surveillance; they’re the ones that have to go arrest these guys, you know, at least confront them, see what they’re doing. I have to tell people listening to this, this is a very careful, indeed conservative, in the best sense of the word, book. This is not a book you can just dismiss by saying it’s got some wild, interesting theory. No—you err, I would say, on the side of caution, in a way.
JD: We err on the side of caution all the time, and we’re not going to try to say something that we can’t really, really defend. If we start from a position that there’s some level of merit to what Clarke is suggesting, that there is this operation going on to try to monitor these hijackers domestically by the CIA, as opposed to handing it off to the FBI—presuming he’s right on that, there is this—
RS: Can I just add a little note that Wilkerson actually goes further.
JD: Wilkerson later suggests that he heard it mentioned after the fact, in about 2003 or 2004, when he is at the CIA. The invasion of Iraq has begun, and they’re waiting for updated satellite information, everyone’s kind of standing around just kind of BS’ing. And he basically overhears a conversation about how, oh man, Tenet tried to flip these guys in the U.S. and then had to hide it because it all went wrong, and it would have come back to bite him. And yeah, Wilkerson basically claims to have overheard high-level people speaking about that, just sort of in a B.S. session.
RN: Well, and not really, not overheard; it’s more like, he claimed multiple, very high-level under Tenet sources, that he was close with at that time, who were in these “yak-yak sessions,” that he calls them. And they each claimed to be aware of the reality of this, supposedly.
JD: You’re asking, like, how nefarious it is. In the first period of all this, presuming that it’s true, presuming that there’s this operation going on to try to flip these guys or follow them or whatever, gather information on them domestically, you can imagine that, OK, they’re going to have some sort of setup in which to monitor these guys, or they’re using Saudi proxies perhaps, or other proxies, and they’re following them. Then we get to this point where, well, the attack succeeds on September 11, so how the heck does that happen? If you have this, if you’re monitoring these guys and then they do this, where does the ball get dropped? And our book does go into that a bit, and we definitely say, like, there’s this moment where they must have said: OK. This isn’t working, it’s not happening, there has got to be a point where they say, abandon ship. But what do they do? How do they abandon ship? They need to somehow turn this over to the FBI to wrap it up for them. And the way they seem to do this is not by being honest and saying, hey, we were trying to do this and it didn’t work, but here’s the information—go get ‘em. They definitely don’t do that.
RS: The “trying to do this”—you mean to turn these terrorists into agents for themselves?—
JD: So what I’m saying is, if at some point when it’s not working, when the flip hasn’t happened, when whatever goal they set for themselves, when they haven’t achieved it, a time must come for them to wrap up this operation. A time must—you can’t just let them go all the way and succeed in their attack, you would think.
RN: But I think what you’re asking is the intention of the operation, which would seem—well, the CIA was created in order to prevent future Pearl Harbors. So I guess, giving them the benefit of the doubt, the intention of the operation would theoretically have been to monitor these guys so as to figure out what they’re doing here in the U.S.
JD: Yes, yes. We’re giving them the benefit of the doubt there. And then we look at the emails and cable traffic we can find in that summer, and we watch as—there’s no search for these guys, there’s no FBI search for these guys until August 23rd of 2001. And that’s the point where, surreptitiously, someone stationed at Alec Station, the Bin Laden unit, CIA, who’s going through old cable traffic, goes: Oh my gosh! I found a cable that these guys came to the United States. And she alerts the FBI, and the FBI begins their domestic search. I guess what I’m suggesting is, a time would have come when they, when whoever is running this operation at the CIA, whatever the architecture of that operation looks like, they would have seen these things happening. They would have seen the connections they were making with these other guys coming to the United States. And a time would have come for them to say: OK. We have to pass this off to the FBI to shut it down. And it does—
RS: But wait a minute. When you say OK, and they’ve seen things—they see people who are identified as terrorists, part of this terrorist network, traces back to Al Qaeda. And they are learning about airplanes and how to fly them, and flight paths, and everything. And you’re telling me that they say, well, you know, maybe we’re not going to actually recruit them, maybe we’re—we better do something. Why aren’t they saying, holy cow, these guys can do great damage to this country! We got to call, what, the local San Diego police, at least, to get them to check them out! No?
RN: OK, so these guys arrive in early 2000. What happens in October 2000? The U.S.S. Cole is attacked in Yemen. FBI agents working that from top levels of the New York office of the FBI find a very direct connection not only to Al Qaeda, but to that same planning meeting that the CIA monitored. The same one where Mihdhar and Hazmi were at that planning meeting. So not only do you have an inclination—oh, these guys are Al Qaeda, they’re probably not here to, in the words of one person, go to f’ing Disneyland. They’re here for something nefarious—but now, after October 2000, for the entire year up to 9/11, the CIA has the knowledge that these two individuals that were at this meeting, that the meeting spawned the U.S.S. Cole attack, which killed 17 dead servicemen. So I think at that point, yeah, calling the local San Diego police would probably make a lot of sense.
RS: OK, and what about the FBI informant who was their link in San Diego? Why isn’t he telling anyone, or why doesn’t the FBI know?
JD: You have to be careful to separate what’s going on at different agencies. An FBI informant’s not necessarily reporting to the CIA, and the CIA informant’s not reporting to the FBI. And then you also have to understand that the FBI has national headquarters and then a bunch of different field offices throughout the country. And you have field office reports coming in, like the Phoenix memo from Ken Williams mentioning that there’s these, all these Muslim guys trying to learn to fly. You’ve got what Coleen Rowley exposes out of Minnesota, when they bust Zacarias Moussaoui, and how they’re trying to get into his laptop, and they’re being hampered by FBI headquarters. So I mean, you don’t know what came from Abdussattar. But I don’t want to move too far into the weeds and off the general thrust of your original question. And I think what you come down to is a fork in the road. At some point, either the CIA running this operation has to wrap it up, or this major attack is going to succeed. If you ask yourself, well, why didn’t they wrap it up—because obviously they didn’t, and the attack did succeed–so if you ask yourself why didn’t they, there’s one potential answer, which is that they were afraid of being prosecuted. Because they had been running an illegal operation in the United States. So their own fear for their own lives, freedom, careers, all that stuff–
RS: For people who don’t understand the law, you have to explain, the CIA was prevented from running this kind of operation domestically. This is supposed to be up to the FBI.
JD: It is a crime for them to operate within the United States.
RN: And what Richard Clarke told us, we don’t know how much of the information, like the Phoenix memo and these other things that Duffy just mentioned, got to George Tenet. But what we do know, the existence of Mihdhar and Hazmi in this country should have made it to him by that point. Because his own CIA counterterror office had informed the FBI in August, and a search had begun. So that information should have been in Tenet’s head. We know that he was briefed about Zacarias Moussaoui acting weird at a flight school in Minnesota. And he comes to the—oh, man —
JD: September 4th principals meeting.
RN: — September 4th principals meeting in the White House. Clarke has been pushing the entire Bush administration, the entire eight, nine months, to be able to brief them on Al Qaeda and make the case for why the administration should take this seriously. And he’s finally got that meeting, and George Tenet is sitting there, and he doesn’t say a word. And he was later asked by investigators why not, and he gave this really bizarre non-answer, which was just like: it just wasn’t the right time, right place, I just can’t take you any further than that. And they let him get away with leaving it at that, but Richard Clarke says the reason he doesn’t tell us at that point, he believes, is because Clarke would have had him brought up on charges that day for malfeasance and misfeasance in withholding that information. Because remember, that would also make his people culpable for the Cole, because they would have known about the planning session for the Cole nine months before that one happened, too. So it looks like —
JD: And then they would have been guilty of obstruction of justice for all of the hiding of these figures once the FBI investigation into the Cole happened. So they have a long list of things they become guilty of should they just turn this over and say, like: Ah, hey guys, there’s these guys, you should probably go do something about it. Now, that’s one explanation. Other people have other explanations. But as I said, we don’t make accusations that we cannot really, firmly back up. So this time, that’s pretty much the one we typically go with.
RS: Two people in your book who take it further are Richard Clarke and Larry Wilkerson. Two of the most highly experienced, knowledgeable individuals to come out of our whole military intelligence complex. And they, put it in human terms, they say they don’t know how these people sleep at night. Wilkerson, even more than Clarke, suggests that these people could have prevented 9/11, and knew about it. Now, I just want to ask you about one other person. Again, the book is devastating; it’s called “The Watchdogs Didn’t Bark: The CIA, NSA, and the Crimes of the War on Terror,” John Duffy and Ray Nowosielski. But let me push it one step further to the contemporary moment. The book is kind of easy on the FBI. But the fact is the FBI was really the agency that should have been following these terrorists when they’re in the United States. But one guy who comes up in current making of history, and who was head of the FBI at a critical point, is Mueller, who’s now running the Russian, interference in our election investigation. What was his role? I’d like to conclude on that, because he’s a major figure right now, the head of this special investigation. What was his role in this?
RN: I mean, it is important to remember that the guy came in, I think it was maybe 10 days before 9/11, and took over the FBI. So he was, among the CIA, NSA, and FBI, he was able to be the only one at the leadership helm in the post-9/11 days and months who you couldn’t really lay any culpability at his door for any kind of failure. Remember, the CIA director George Tenet, he’s right at the table with the President; he’s a Cabinet-level guy. The FBI director, it’s not the same way. The FBI director reports to the Attorney General in the Department of Justice, and the Attorney General gets the direct seat. We make the case in the book that when George Tenet, in the week after 9/11, made the big play, the big power grab for the CIA, what we call the wish list of every CIA director accumulated over the whole history of the agency, and essentially puts it out there to Bush and says, these are the powers we need now to make sure this kind of thing doesn’t happen—he gets his green light. Mueller, on the other hand—well, a couple things happen. For one thing, the stories–the CIA is better at keeping their skeletons hidden, for a while. So the first stories that come out that start to paint a picture of blame regarding 9/11, they’re all pointing towards the FBI. Coleen Rowley comes out, and she points a finger at Mueller in May of 2002, and that sort of gets the ball rolling on the “it was the FBI’s fault” story, which really didn’t get corrected for quite a number of years. So our sources tell us Mueller was playing defense, he was willing to kind of go along as the Bush administration pushed that–we kind of know what happened here, so we don’t need to investigate this much further; you should be putting your FBI resources towards preventing future attacks. And I can certainly understand why a man like Robert Mueller in that position would say, would not want to be the guy that missed the next one. So from what we can tell, and from what our sources told us, it does seem that he sort of wrapped up the 9/11 investigation, or just ended it midway. But what was happening was, we talked with Pat DeMoro—he was one of our sources—and he took us inside, he ran the 9/11 criminal investigation; remember, this was a crime, right. At least 19 guys, probably a lot more, were involved in a plot that resulted in 3,000 murders. So he was investigating that, and he was finding over about a two-year period, there would be leads that would point towards Saudi facilitators to the hijackers, Saudi helpers, Saudi royal money coming over. And every time he found these, he had to report them up to Bob Mueller. Bob Mueller would theoretically report them to the Attorney General, who would theoretically report them to Bush. And yet the end result of this was that Bush invades Iraq, and the U.S. public never heard about these Saudi connections until, officially, until just a couple of years ago, really.
JD: And you have said that our book comes off pretty light on the FBI, and I think the crucial difference to make clear is that most of the people we’re talking about within the FBI are from particularly one field office. We’re talking about John O’Neill’s people out of New York, who are counterterror investigators. That’s most of the people we’re dealing—we’re not, we mention a few other people from FBI headquarters, but we don’t necessarily mention them in the best light. And one of the big failures of the FBI is the search to find al-Mihdhar and al-Hazmi, once they are made aware that they’re in the country a couple weeks before 9/11. And that is a huge story there, and we could only write so much book. So we don’t want to just sit here and say, like, oh, the FBI is great and did everything right; we focus specifically on a handful of people who did do their damnedest to unearth the conspirators behind the Cole attack, and to pass information about the presence of al-Mihdhar and al-Hazmi over to FBI investigators in New York in the runup to 9/11. So we don’t want to necessarily sit here and say the FBI was perfect and did everything right; we’re talking about a handful of individuals.
RS: And as you’ve just indicated, your style and the character of this book is quite scholarly. It’s very thoughtful, it’s incredibly well documented. And you got people really on the inside, in the know, to trust you and to talk honestly about it. You’ve done the gumshoe journalism, you took 10 years, you checked every record. What has been the critical response?
RN: Well, we should have put Trump’s picture on the cover. [Laughs] I think that would have helped.
RS: That’s a pretty profound observation, in a way. Because there’s a whole bunch of people now who think all of our troubles in this country started and will end with Trump. And it really whitewashes everybody else.
JD: It’s whitewashing a lot of people. There’s, all of a sudden people who a few years ago we were like, this is the worst person on earth!—like George W. Bush, is now just being embraced by Democrats as some, like, affable guy. All the crimes of the war on terror, the torture, Abu-Ghraib, it’s all just gone—the unnecessary invasion of the war in Iraq, it’s all just sort of under the rug now because of Trump.
RS: Yeah, those were the adults watching the store. Everybody is angry that Trump doesn’t have adults watching the store, and now he just got in trouble with his Secretary of Defense, pushing him out, and now that guy is whitewashed, right? He was considered a mad dog at one point. So you’re right; your book has run into a head storm of indifference to anything that happened before Trump. But I’m asking a very pointed question. What happens? You guys spent over 10 years on this, right?
RN: Yeah. And you know, our goal was not to get famous. [Laughs] We really did want accountability for this small group of people that we thought, these people cannot stay in the CIA, right? We’re not going to keep letting them run the War on Terror, are we? And maybe if people just know about this, or if we can just prove it–if we talk with enough insiders, if we get enough documents together, if we write a book. It turns out, no. There’s going to be no accountability, and they’re going to, the few that remain now at high levels of the CIA are going to continue to do what they do, and no one’s going to know about it except for folks that listen to your show, so thank you.
RS: Well, they’re going to write the history. I mean, the amazing thing–you think of a movie like “Zero Dark Thirty,” you know; and you quote John Kiriakou in your book, and he was in the CIA; he was actually very successful in being involved with the capture of the highest person connected with al-Qaida, and so forth. And they spun a myth that the torture worked, and you needed torture, and blah blah blah. And it basically went unchallenged. So these people who either lied, or just lied by not talking, even to the FBI or the White House—they get to control the narrative. And then a book like yours comes out, and—I’m asking a very serious question. What has been the response of The New York Times, The Washington Post?
JD: [Laughing] We’re still waiting to hear what The Washington Post and The New York Times think. We’ve gotten a lot of praise from people who have read it, but we’re not getting any really major national or international reviews. Well, one thing we like to do, you mentioned “Zero Dark Thirty.” And the main character, played by Jessica Chastain, is sort of an amalgamation of a handful of people who did work at the CIA, most prominently a woman by the name of Alfreda Bikowsky, who is mentioned very prominently in our book. We want people to know her name, Alfreda Bikowsky, because it’s a name that was sort of an open secret in the media in, you know, New York, Washington, for many, many years. Her involvement goes from the pre-9/11 period there at Alec Station through torture and drone killings, and we want to make sure that her name gets out there so she can’t hide in the shadows.
RN: Her name was never mentioned in any media until it came out on our website. It was 11 years, 10 months from the first alleged crime she’d committed that we documented, until her name came out on our website.
JD: We just like to throw her name out there every once in a while, and make sure more and more people hear it.
RS: Ah, that should be enough to inspire people to get a copy of “The Watchdogs Didn’t Bark: The CIA, NSA, and the Crimes of the War on Terror.” It’s written by John Duffy and Ray Nowosielski. It’s a very, very important book. This is the yeoman journalistic work on the story, and it’s informed by people on the inside who really witnessed it, and were shocked by what they saw, high-level people. So I recommend the book. I want to thank you guys for coming on. OK, that’s it for this edition of Scheer Intelligence. Our engineers at KCRW are Kat Yore and Mario Diaz. Our producers are Joshua Scheer and Isabel Carreon. I’m Robert Scheer, and we’re doing this broadcast from the University of Southern California Annenberg School for Communication and Journalism, where Sebastian Grubaugh, as he often does, has made the show work, and I want to thank him.

via ZeroHedge News http://bit.ly/2DCimC5 Tyler Durden